Biotechnological approaches to enhance salidroside, rosin and its derivatives production in selected Rhodiola spp. in vitro cultures
- PMID: 26213525
- PMCID: PMC4513219
- DOI: 10.1007/s11101-014-9368-y
Biotechnological approaches to enhance salidroside, rosin and its derivatives production in selected Rhodiola spp. in vitro cultures
Abstract
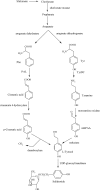
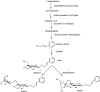
Rhodiola (Crassulaceae) an arctic-alpine plant, is extensively used in traditional folk medicine in Asian and European countries. A number of investigations have demonstrated that Rhodiola preparations exhibit adaptogenic, neuroprotective, anti-tumour, cardioprotective, and anti-depressant effects. The main compounds responsible for these activities are believed to be salidroside, rosin and its derivatives which became the target of biotechnological investigations. This review summarizes the results of the diverse biotechnological approaches undertaken to enhance the production of salidroside, rosin and its derivatives in callus, cell suspension and organ in vitro cultures of selected Rhodiola species.
Keywords: Biotransformation; In vitro cultures; Rhodiola spp.; Rosin derivatives; Salidroside.
Figures
References
-
- Abidov M, Crendal F, Grachev S, Seifulla R, Ziegenfuss T. Effect of extracts from Rhodiola rosea and Rhodiola crenulata (Crassulaceae) roots on ATP content in mitochondria of skeletal muscles. Bull Exp Med. 2003;136(6):585–587. - PubMed
-
- Akgul Y, Ferreira D, Abourashed EA, Khan IA. Lotaustralin from Rhodiola rosea roots. Fitoterapia. 2004;75:612–614. - PubMed
-
- Ali Z, Fronczek FR, Khan IA. Phenylalkanoids and monoterpene analogues from the roots of Rhodiola rosea. Planta Med. 2008;74:178–181. - PubMed
-
- Altantsetseg K, Przybył J, Węglarz Z, Geszprych A. Content of biologically active compounds in roseroot (Rhodiola spp.) raw material of different derivation. Herba Pol. 2007;53(4):20–26.
-
- Bozhilova M. Salidroside content in Rhodiola rosea L., dynamics and variability. Bot Serb. 2011;35(1):67–70.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous