Differential expression of microRNA-206 and its target genes in preeclampsia
- PMID: 26213997
- PMCID: PMC4570688
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000656
Differential expression of microRNA-206 and its target genes in preeclampsia
Abstract
Objectives: Preeclampsia is a multisystem disease that significantly contributes to maternal and foetal morbidity and mortality. In this study, we used a nonbiased microarray approach to identify novel circulating miRNAs in maternal plasma that may be associated with preeclampsia.
Methods: Plasma samples were obtained at 16 and 28 weeks of gestation from 18 women who later developed preeclampsia (cases) and 18 matched women with normotensive pregnancies (controls). We studied miRNA expression profiles in plasma and subsequently confirmed miRNA and target gene expression in placenta samples. Placental samples were obtained from an independent cohort of 19 women with preeclampsia matched with 19 women with normotensive pregnancies.
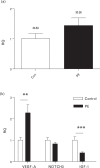
Results: From the microarray, we identified one miRNA that was significantly differentially expressed between cases and controls at 16 weeks of gestation and six miRNAs that were significantly differentially expressed at 28 weeks. Following qPCR validation, only one miR-206 was found to be significantly increased in 28-week samples in women who later developed preeclampsia (1.4-fold change ± 0.2). The trend for increase in miR-206 expression was mirrored within placental tissue from women with preeclampsia. In parallel, IGF-1, a target gene of miR-206, was also found to be downregulated (0.41 ± 0.04) in placental tissue from women with preeclampsia. miR-206 expression was also detectable in myometrium tissue and trophoblast cell lines.
Conclusion: Our pilot study has identified miRNA-206 as a novel factor upregulated in preeclampsia within the maternal circulation and in placental tissue.
Figures

References
-
- Steegers EA, von Dadelszen P, Duvekot JJ, Pijnenborg R. Preeclampsia. Lancet 2010; 376:631–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

