Integration of multimodal neuroimaging methods: a rationale for clinical applications of simultaneous EEG-fMRI
- PMID: 26214023
- PMCID: PMC4520679
Integration of multimodal neuroimaging methods: a rationale for clinical applications of simultaneous EEG-fMRI
Abstract
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which has high spatial resolution, is increasingly used to evaluate cerebral functions in neurological and psychiatric diseases. The main limitation of fMRI is that it detects neural activity indirectly, through the associated slow hemodynamic variations. Because neurovascular coupling can be regionally altered by pathological conditions or drugs, fMRI responses may not truly reflect neural activity. Electroencephalography (EEG) recordings, which directly detect neural activity with optimal temporal resolution, can now be obtained during fMRI data acquisition. Therefore, there is a growing interest in combining the techniques to obtain simultaneous EEG-fMRI recordings. The EEG-fMRI approach has several promising clinical applications. The first is the detection of cortical areas involved in interictal and ictal epileptic activity. Second, combining evoked potentials with fMRI could be an accurate way to study eloquent cortical areas for the planning of neurosurgery or rehabilitation, circumventing the above-mentioned limitation of fMRI. Finally, the use of this approach to evaluate the functional connectivity of resting-state networks would extend the applications of EEG-fMRI to uncooperative or unconscious patients. Integration of multimodal neuroimaging methods: a rationale for clinical applications of simultaneous EEG-fMRI.
Figures
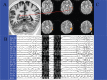
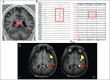
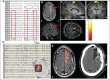
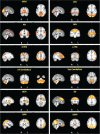
References
-
- Allen PJ, Josephs O, Turner R. A method for removing imaging artifact from continuous EEG recorded during functional MRI. Neuroimage. 2000;12:230–239. - PubMed
-
- Allen PJ, Polizzi G, Krakow K, et al. Identification of EEG events in the MR scanner: the problem of pulse artifact and a method for its subtraction. Neuroimage. 1998;8:229–239. - PubMed
-
- Anwar MN, Bonzano L, Sebastiano DR, et al. Real-time artifact filtering in continuous VEPs/fMRI recording. J Neurosci Methods. 2009;184:213–223. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann CF, Smith SM. Tensorial extensions of independent component analysis for multisubject FMRI analysis. Neuroimage. 2005;25:294–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
