Generation of vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells from human pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 26214132
- PMCID: PMC4566857
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3205
Generation of vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells from human pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
The use of human pluripotent stem cells for in vitro disease modelling and clinical applications requires protocols that convert these cells into relevant adult cell types. Here, we report the rapid and efficient differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. We found that GSK3 inhibition and BMP4 treatment rapidly committed pluripotent cells to a mesodermal fate and subsequent exposure to VEGF-A or PDGF-BB resulted in the differentiation of either endothelial or vascular smooth muscle cells, respectively. Both protocols produced mature cells with efficiencies exceeding 80% within six days. On purification to 99% via surface markers, endothelial cells maintained their identity, as assessed by marker gene expression, and showed relevant in vitro and in vivo functionality. Global transcriptional and metabolomic analyses confirmed that the cells closely resembled their in vivo counterparts. Our results suggest that these cells could be used to faithfully model human disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
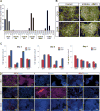

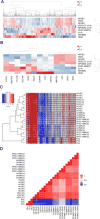
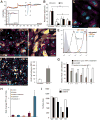
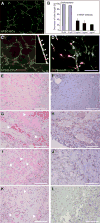
References
-
- Thomson JA, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL106018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100408/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL106018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01 DK53298/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK049216/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL100408/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL048801/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK092760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL04880/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 DK097768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01 HL10001-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01DK081572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053298/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK097768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30 DK49216/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL60963/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL083867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

