Estimating the Number of Heterosexual Persons in the United States to Calculate National Rates of HIV Infection
- PMID: 26214309
- PMCID: PMC4516312
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133543
Estimating the Number of Heterosexual Persons in the United States to Calculate National Rates of HIV Infection
Abstract
Background: This study estimated the proportions and numbers of heterosexuals in the United States (U.S.) to calculate rates of heterosexually acquired human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Quantifying the burden of disease can inform effective prevention planning and resource allocation.
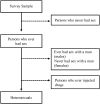
Methods: Heterosexuals were defined as males and females who ever had sex with an opposite-sex partner and excluded those with other HIV risks: persons who ever injected drugs and males who ever had sex with another man. We conducted meta-analysis using data from 3 national probability surveys that measured lifetime (ever) sexual activity and injection drug use among persons aged 15 years and older to estimate the proportion of heterosexuals in the United States population. We then applied the proportion of heterosexual persons to census data to produce population size estimates. National HIV infection rates among heterosexuals were calculated using surveillance data (cases attributable to heterosexual contact) in the numerators and the heterosexual population size estimates in the denominators.
Results: Adult and adolescent heterosexuals comprised an estimated 86.7% (95% confidence interval: 84.1%-89.3%) of the U.S. population. The estimate for males was 84.1% (CI: 81.2%-86.9%) and for females was 89.4% (95% CI: 86.9%-91.8%). The HIV diagnosis rate for 2013 was 5.2 per 100,000 heterosexuals and the rate of persons living with diagnosed HIV infection in 2012 was 104 per 100,000 heterosexuals aged 13 years or older. Rates of HIV infection were >20 times as high among black heterosexuals compared to white heterosexuals, indicating considerable disparity. Rates among heterosexual men demonstrated higher disparities than overall population rates for men.
Conclusions: The best available data must be used to guide decision-making for HIV prevention. HIV rates among heterosexuals in the U.S. are important additions to cost effectiveness and other data used to make critical decisions about resources for prevention of HIV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2015). HIV Surveillance Report, 2013. vol. 25. Available: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/reports/surveillance. Published February 2015. Accessed 2015 May.
-
- Lansky A, Finlayson T, Johnson C, Holtzman D, Wejnert C, Mitsch A, et al. (2014). Estimating the number of persons who inject drugs in the United States by meta-analysis to calculate national rates of HIV and Hepatitis C Virus infections. PLoS One, 9(5), e97596 10.1371/journal.pone.0097596 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- SUDAAN, release 9.1. [computer program]. (2004). Research Triangle Park, NC: RTI International.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical