Pharmacological evidence for a role of the transient receptor potential canonical 3 (TRPC3) channel in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis of human coronary artery endothelial cells
- PMID: 26215710
- PMCID: PMC4706806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vph.2015.07.011
Pharmacological evidence for a role of the transient receptor potential canonical 3 (TRPC3) channel in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis of human coronary artery endothelial cells
Abstract
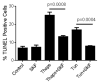
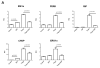
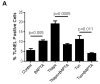
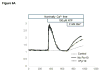
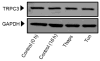
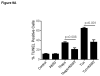
Unresolved endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, with the subsequent persistent activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) is a well-recognized mechanism of endothelial cell apoptosis with a major impact on the integrity of the endothelium during the course of cardiovascular diseases. As in other cell types, Ca(2+) influx into endothelial cells can promote ER stress and/or contribute to mechanisms associated with it. In previous work we showed that in human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) the Ca(2+)-permeable non-selective cation channel Transient Receptor Potential Canonical 3 (TRPC3) mediates constitutive Ca(2+) influx which is critical for operation of inflammatory signaling in these cells, through a mechanism that entails coupling of TRPC3 constitutive function to activation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMKII). TRPC3 has been linked to UPR signaling and apoptosis in cells other than endothelial, and CAMKII is a mediator of ER stress-induced apoptosis in various cell types, including endothelial cells. In the present work we used a pharmacological approach to examine whether in HCAECs TRPC3 and CAMKII also contribute to mechanisms of ER stress-induced apoptosis. The findings show for the first time that in HCAECs activation of the UPR and the subsequent ER stress-induced apoptosis exhibit a strong requirement for constitutive Ca(2+) influx and that TRPC3 contributes to this process. In addition, we obtained evidence indicating that, similar to its roles in non-endothelial cells, CAMKII participates in ER stress-induced apoptosis in HCAECs.
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Endothelial cell apoptosis; TRPC3 channels.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






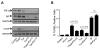

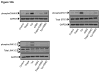

References
-
- Baldi CVG, Boland R. Capacitative calcium influx in human epithelial breast cancer and non-tumorigenic cells occurs through Ca2+ entry pathways with different permeabilities to divalent cations. Journal of cellular biochemistry. 2003;88:1265–1272. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, He FF, Wang H, Fang Z, Shao N, Tian XJ, Liu JS, Zhu ZH, Wang YM, Wang S, Huang K, Zhang C. Calcium entry via TRPC6 mediates albumin overload-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in podocytes. Cell calcium. 2011;50:523–529. - PubMed
-
- Hollien J. Evolution of the unfolded protein response. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 2013;1833:2458–2463. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

