Bevacizumab promotes venous thromboembolism through the induction of PAI-1 in a mouse xenograft model of human lung carcinoma
- PMID: 26215730
- PMCID: PMC4517418
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-015-0418-x
Bevacizumab promotes venous thromboembolism through the induction of PAI-1 in a mouse xenograft model of human lung carcinoma
Abstract
Background: An increased incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is associated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) treatment in cancer. However, the mechanism underlying this effect remains elusive. In this study, we examined the effect of bevacizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody against VEGF-A, on VTE in a murine xenograft A549 cell tumor model.
Methods: Inferior vena cava stenosis model and FeCl3-induced saphenous vein thrombosis model were performed in a mouse xenograft models of human lung adenocarcinoma.
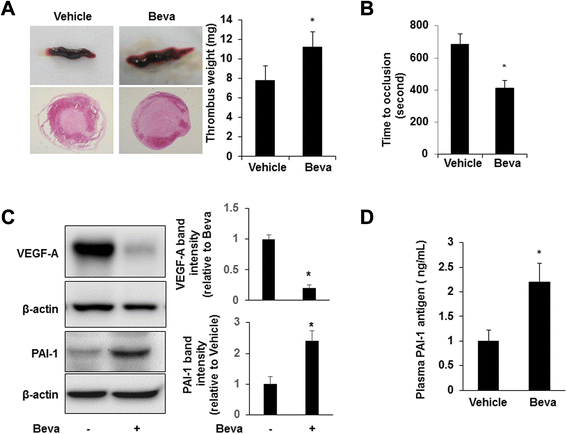
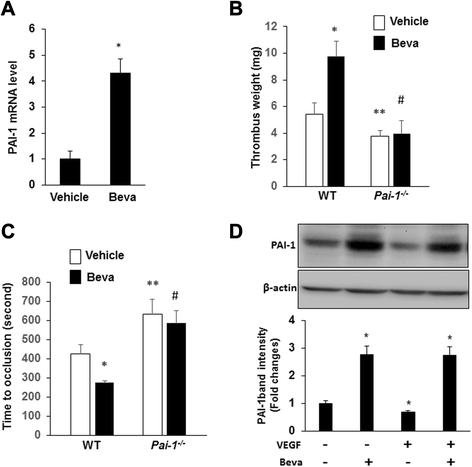
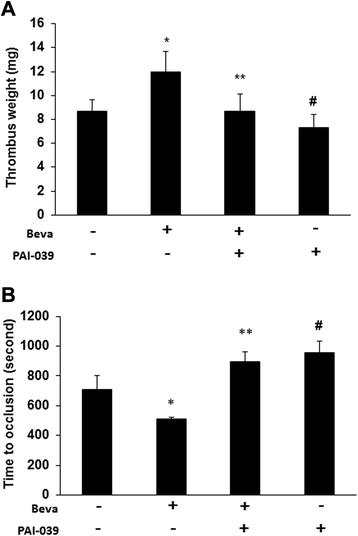
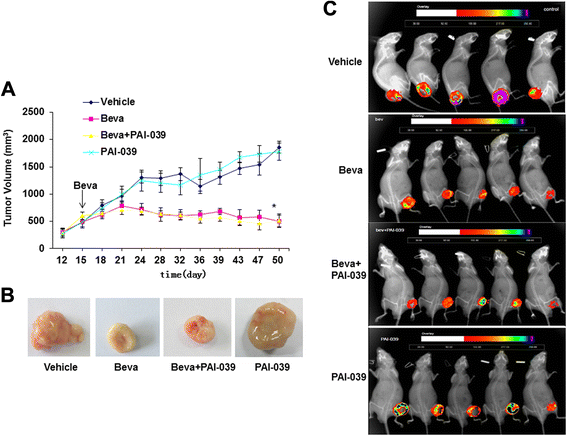
Results: We found that treatment with bevacizumab significantly increased the thrombotic response to inferior vena cava obstruction and femoral vein injury. Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) expression in tumors, plasma, and thrombi was significantly increased by bevacizumab. However, bevacizumab did not enhance VTE in PAI-1-deficient mice, suggesting that PAI-1 is a major mediator of bevacizumab's prothrombotic effect. VEGF inhibited expression of PAI-1 by A549 cells, and this effect was neutralized by bevacizumab, suggesting that bevacizumab increases PAI-1 expression in vivo by blocking the inhibitory effect of VEGF on PAI-1 expression by tumor cells. Pharmacological inhibition of PAI-1 with PAI-039 blocked bevacizumab-induced venous thrombosis.
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings indicate that PAI-1 plays a role in VTE associated with antiangiogenic therapy and the inhibition of PAI-1 shows efficacy as a therapeutic strategy for the prevention of bevacizumab-associated VTE.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

