Membrane-mediated amyloid formation of PrP 106-126: A kinetic study
- PMID: 26215743
- PMCID: PMC4554819
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.07.014
Membrane-mediated amyloid formation of PrP 106-126: A kinetic study
Abstract
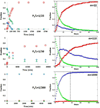
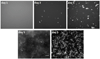
PrP 106-126 conserves the pathogenic and physicochemical properties of the Scrapie isoform of the prion protein. PrP 106-126 and other amyloidal proteins are capable of inducing ion permeability through cell membranes, and this property may represent the common primary mechanism of pathogenesis in the amyloid-related degenerative diseases. However, for many amyloidal proteins, despite numerous phenomenological observations of their interactions with membranes, it has been difficult to determine the molecular mechanisms by which the proteins cause ion permeability. One approach that has not been undertaken is the kinetic study of protein-membrane interactions. We found that the reaction time constant of the interaction between PrP 106-126 and membranes is suitable for such studies. The kinetic experiment with giant lipid vesicles showed that the membrane area first increased by peptide binding but then decreased. The membrane area decrease was coincidental with appearance of extramembranous aggregates including lipid molecules. Sometimes, the membrane area would increase again followed by another decrease. The kinetic experiment with small vesicles was monitored by circular dichroism for peptide conformation changes. The results are consistent with a molecular simulation following a simple set of well-defined rules. We deduced that at the molecular level the formation of peptide amyloids incorporated lipid molecules as part of the aggregates. Most importantly the amyloid aggregates desorbed from the lipid bilayer, consistent with the macroscopic phenomena observed with giant vesicles. Thus we conclude that the main effect of membrane-mediated amyloid formation is extraction of lipid molecules from the membrane. We discuss the likelihood of this effect on membrane ion permeability.
Keywords: Amyloidal peptides; Circular dichroism; Giant unilamellar vesicles; Lipid extracting effect; Neurodegenerative diseases; Prion protein.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Perutz MF, Windle AH. Cause of neural death in neurodegenerative diseases attributable to expansion of glutamine repeats. Nature. 2001;412:143–144. - PubMed
-
- Lashuel HA, Lansbury PT., Jr Are amyloid diseases caused by protein aggregates that mimic bacterial pore-forming toxins? Q Rev Biophys. 2006;39:167–201. - PubMed
-
- Caughey B, Lansbury PT. Protofibrils, pores, fibrils, and neurodegeneration: separating the responsible protein aggregates from the innocent bystanders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:267–298. - PubMed
-
- Kodali R, Wetzel R. Polymorphism in the intermediates and products of amyloid assembly. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2007;17:48–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

