D-dimer for the exclusion of cerebral venous thrombosis: a meta-analysis of low risk patients with isolated headache
- PMID: 26215857
- PMCID: PMC4517419
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-015-0389-y
D-dimer for the exclusion of cerebral venous thrombosis: a meta-analysis of low risk patients with isolated headache
Abstract
Background: Patients with isolated headache may have cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT). D-dimers are proven sensitive in excluding deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in low risk patients. We aimed to determine whether D-dimer may play the same role in low risk CVT patients with isolated headache.
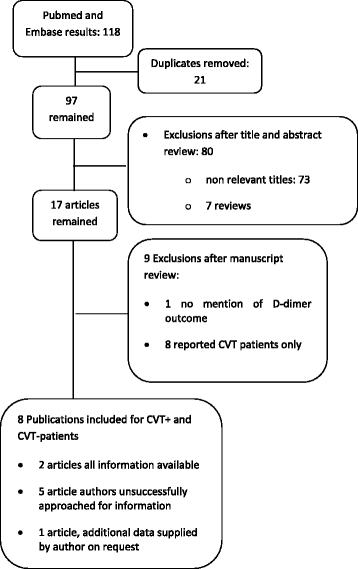
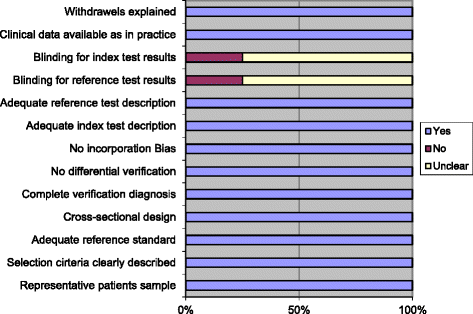
Methods: We included consecutive patients suspected of CVT from our teaching hospital with isolated headache, a normal neurological examination and normal standard head CT in whom D-dimer was determined. Additionally we did a systematic review on articles describing consecutive patients suspected of CVT with isolated headache and their D-dimer values. CVT was investigated with CT or MR venography in all patients.
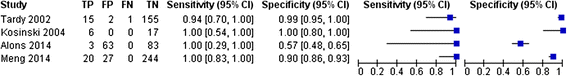
Results: A total of 636 consecutive patients were collected from our own data and the literature search. Of 45 CVT patients one had a negative D-dimer (7.5 %). Sensitivity of D-dimer for diagnosing CVT was 97.8 % (95 % CI: 88.2-99.6 %), specificity was 84.9 % (95 % CI: 81.8-87.7 %), positive predictive value was 33.1 % (95 % CI: 25.2-41.7 %), negative predictive value was 99.8 % (95 % CI: 98.9-100 %). Another 56 isolated headache CVT patients were identified in literature, lacking consecutive isolated headache controls. Sensitivity of D-dimer for diagnosing CVT including these patients was 87.1 % (95 % CI: 79.0-93.0 %).
Conclusions: D-dimers have a high negative predictive value in patients with isolated headache for excluding CVT. Sensitivity is lower but comparable to the values accepted in PE and DVT. Low risk patients were defined as headache patients with a normal neurological examination, normal standard head CT and absence of risk factors such as pregnancy or puerperium. Normal D-dimers in these patients may reduce unnecessary imaging, making it a potential valuable marker.
Figures
Similar articles
-
D-dimer testing in the diagnosis of cerebral vein thrombosis: a systematic review and a meta-analysis of the literature.J Thromb Haemost. 2012 Apr;10(4):582-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04637.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22257124
-
D-dimer test for excluding the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 5;2016(8):CD010864. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010864.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27494075 Free PMC article.
-
D-dimer for the exclusion of acute venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a systematic review.Ann Intern Med. 2004 Apr 20;140(8):589-602. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-8-200404200-00005. Ann Intern Med. 2004. PMID: 15096330
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 16;5(5):CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35575286 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictive Value of Combination of D-dimer and Fibrinogen in Diagnosing Acute CVST.Ann Neurosci. 2021 Jul;28(3-4):156-161. doi: 10.1177/09727531211063138. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Ann Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 35341225 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic utility of unenhanced computed tomography of the brain and D-dimer levels in acute cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A quantitative study.J Clin Imaging Sci. 2022 Apr 16;12:15. doi: 10.25259/JCIS_76_2021. eCollection 2022. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2022. PMID: 35510244 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Clin Pract. 2021 Sep 7;11(3):598-606. doi: 10.3390/clinpract11030075. Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 34563004 Free PMC article.
-
C-reactive protein and D-dimer in cerebral vein thrombosis: Relation to clinical and imaging characteristics as well as outcomes in a French cohort study.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023 Mar 28;7(3):100130. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.100130. eCollection 2023 Mar. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 37138790 Free PMC article.
-
The Utility of Quantitative D-Dimer Assay as a Biomarker in the Diagnosis and Exclusion of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis.Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2024 Jan;40(1):122-129. doi: 10.1007/s12288-023-01677-8. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2024. PMID: 38312171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferro JM, Canhão P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F, Investigators ISCVT. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT) Stroke. 2004;35:664–70. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000117571.76197.26. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical