Relative Effectiveness of Letrozole Compared With Tamoxifen for Patients With Lobular Carcinoma in the BIG 1-98 Trial
- PMID: 26215945
- PMCID: PMC4550691
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.60.8133
Relative Effectiveness of Letrozole Compared With Tamoxifen for Patients With Lobular Carcinoma in the BIG 1-98 Trial
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the relative effectiveness of letrozole compared with tamoxifen for patients with invasive ductal or lobular carcinoma.
Patients and methods: Patients diagnosed with early-stage invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) or classic invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) who were randomly assigned onto the Breast International Group (BIG) 1-98 trial and who had centrally reviewed pathology data were included (N = 2,923). HER2-negative IDC and ILC were additionally classified as hormone receptor-positive with high (luminal B [LB] -like) or low (luminal A [LA] -like) proliferative activity by Ki-67 labeling index. Survival analyses were performed with weighted Cox models that used inverse probability of censoring weighted modeling.
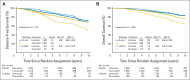
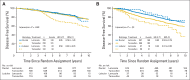
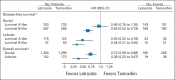
Results: The median follow-up time was 8.1 years. In multivariable models for disease-free survival (DFS), significant interactions between treatment and histology (ILC or IDC; P = .006) and treatment and subgroup (LB like or LA like; P = .01) were observed. In the ILC subset, there was a 66% reduction in the hazard of a DFS event with letrozole for LB (hazard ratio [HR], 0.34; 95% CI, 0.21 to 0.55) and a 50% reduction for LA subtypes (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.32 to 0.78). In the IDC subset, there was a significant 35% reduction in the hazard of a DFS event with letrozole for the LB subtype (HR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.53 to 0.79), but no difference between treatments was noted for IDC and the LA subtype (HR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.76 to 1.20).
Conclusion: The magnitude of benefit of adjuvant letrozole is greater for patients diagnosed with lobular carcinoma versus ductal carcinoma.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00004205.
© 2015 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures

References
-
- Rakha EA, Ellis IO. Lobular breast carcinoma and its variants. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2010;27:49–61. - PubMed
-
- Li CI, Anderson BO, Daling JR, et al. Trends in incidence rates of invasive lobular and ductal breast carcinoma. JAMA. 2003;289:1421–1424. - PubMed
-
- Iorfida M, Maiorano E, Orvieto E, et al. Invasive lobular breast cancer: Subtypes and outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;133:713–723. - PubMed
-
- Metzger Filho O, Michiels S, Bertucci F, et al. Genomic grade adds prognostic value in invasive lobular carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:377–384. - PubMed
-
- Tubiana-Hulin M, Stevens D, Lasry S, et al. Response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in lobular and ductal breast carcinomas: A retrospective study on 860 patients from one institution. Ann Oncol. 2006;17:1228–1233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

