Galectin-1 regulates tissue exit of specific dendritic cell populations
- PMID: 26216879
- PMCID: PMC4566239
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.644799
Galectin-1 regulates tissue exit of specific dendritic cell populations
Abstract
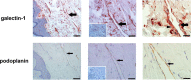
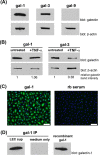
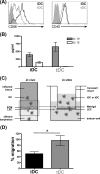
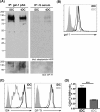
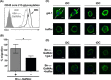
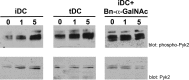
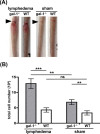
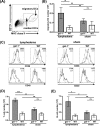
During inflammation, dendritic cells emigrate from inflamed tissue across the lymphatic endothelium into the lymphatic vasculature and travel to regional lymph nodes to initiate immune responses. However, the processes that regulate dendritic cell tissue egress and migration across the lymphatic endothelium are not well defined. The mammalian lectin galectin-1 is highly expressed by vascular endothelial cells in inflamed tissue and has been shown to regulate immune cell tissue entry into inflamed tissue. Here, we show that galectin-1 is also highly expressed by human lymphatic endothelial cells, and deposition of galectin-1 in extracellular matrix selectively regulates migration of specific human dendritic cell subsets. The presence of galectin-1 inhibits migration of immunogenic dendritic cells through the extracellular matrix and across lymphatic endothelial cells, but it has no effect on migration of tolerogenic dendritic cells. The major galectin-1 counter-receptor on both dendritic cell populations is the cell surface mucin CD43; differential core 2 O-glycosylation of CD43 between immunogenic dendritic cells and tolerogenic dendritic cells appears to contribute to the differential effect of galectin-1 on migration. Binding of galectin-1 to immunogenic dendritic cells reduces phosphorylation and activity of the protein-tyrosine kinase Pyk2, an effect that may also contribute to reduced migration of this subset. In a murine lymphedema model, galectin-1(-/-) animals had increased numbers of migratory dendritic cells in draining lymph nodes, specifically dendritic cells with an immunogenic phenotype. These findings define a novel role for galectin-1 in inhibiting tissue emigration of immunogenic, but not tolerogenic, dendritic cells, providing an additional mechanism by which galectin-1 can dampen immune responses.
Keywords: dendritic cell; endothelial cell; extracellular matrix; galectin; inflammation; migration.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Luster A. D., Alon R., von Andrian U. H. (2005) Immune cell migration in inflammation: present and future therapeutic targets. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1182–1190 - PubMed
-
- Ley K., Laudanna C., Cybulsky M. I., Nourshargh S. (2007) Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 678–689 - PubMed
-
- Segura E., Amigorena S. (2013) Inflammatory dendritic cells in mice and humans. Trends Immunol. 34, 440–445 - PubMed
-
- Malissen B., Tamoutounour S., Henri S. (2014) The origins and functions of dendritic cells and macrophages in the skin. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 14, 417–428 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

