Systematic review: Eosinophilic esophagitis in Asian countries
- PMID: 26217096
- PMCID: PMC4507114
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8433
Systematic review: Eosinophilic esophagitis in Asian countries
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the prevalence and the clinical characteristics of Asian patients with eosinophilic esophagitis.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search of the PubMed and Web of Science databases for original studies, case series, and individual case reports of eosinophilic esophagitis in Asian countries published from January 1980 to January 2015. We found 66 and 80 articles in the PubMed and Web of Science databases, respectively; 24 duplicate articles were removed. After excluding animal studies, articles not written in English, and meeting abstracts, 25 articles containing 217 patients were selected for analysis.
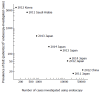
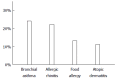
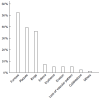
Results: Sample size-weighted mean values were determined for all pooled prevalence data and clinical characteristics. The mean age of the adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis was approximately 50 years, and 73% of these patients were male. They frequently presented with allergic diseases including bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, food allergy, and atopic dermatitis. Bronchial asthma was the most frequent comorbid allergic disease, occurring in 24% of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dysphagia was the primary symptom reported; 44% of the patients complained of dysphagia. Although laboratory blood tests are not adequately sensitive for an accurate diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis, endoscopic examinations revealed abnormal findings typical of this disease, including longitudinal furrows and concentric rings, in 82% of the cases. One-third of the cases responded to proton pump inhibitor administration.
Conclusion: The characteristics of eosinophilic esophagitis in Asian patients were similar to those reported in Western patients, indicating that this disease displays a similar pathogenesis between Western and Asian patients.
Keywords: Allergy; Asia; Endoscopy; Eosinophilic esophagitis; Prevalence; Symptom; Treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, Atkins D, Attwood SE, Bonis PA, Burks AW, Chehade M, Collins MH, Dellon ES, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3–20.e6; quiz 21-22. - PubMed
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: Evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679–692; quiz 693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

