Cardiac natriuretic peptides in plasma increase after dietary induced weight loss in obesity
- PMID: 26217511
- PMCID: PMC4511261
- DOI: 10.1186/s40608-014-0024-2
Cardiac natriuretic peptides in plasma increase after dietary induced weight loss in obesity
Abstract
Background: Cardiac natriuretic peptides are established biomarkers in heart disease, but are also affected by body mass index (BMI). The purpose of the present study was to examine the impact of weight loss and changes in body composition following dietary intervention on plasma concentrations of the prohormones to A- and B-type natriuretic peptides (proANP and proBNP) and adrenomedullin (proADM).
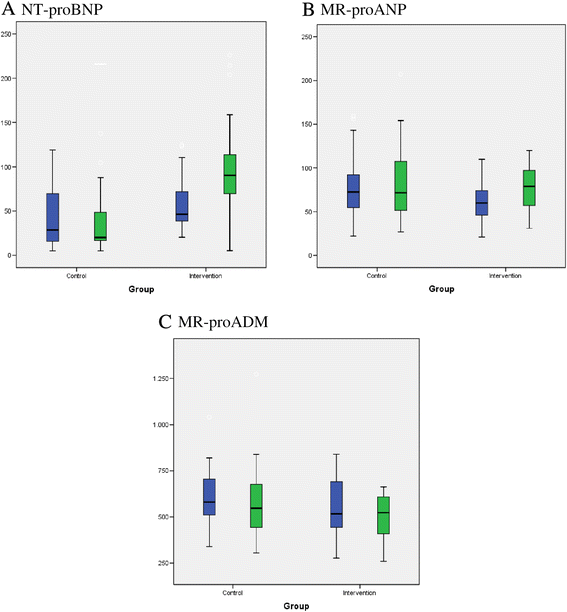
Results: A total of 52 healthy obese subjects, 47 women and 5 men (BMI 36.5 ± 5.6 kg/m(2)) were randomised to either an intensive weight reduction programme using a combination of very low calorie diet (810 kcal/day) and conventional hypo-energetic diet (1200 kcal/day) for 52 weeks, or to a control group that was offered diet-related counselling. N-terminal proBNP (NT-proBNP), mid-regional proANP (MR-proANP) and proADM (MR-proADM) and body composition using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scanning were determined at baseline and after 52 weeks. Comparisons between groups were analysed using t-tests. Changes from the baseline within the groups were analysed with paired tests. Changes in the variables, delta (∆), were calculated as 52 weeks minus the baseline. In the intervention group, BMI decreased by almost 20% (31.6 ± 6.2 vs. 37.1 ± 6.1 kg/m(2); P <0.001) with a loss of body fat of 23.5 ± 15.5% (P < 0.001). Plasma concentrations of NT-proBNP and MR-proANP increased (from 55 ± 31 to 97 ± 55 pg/ml; P < 0.001, and from 59 ± 21 to 74 ± 26 pmol/L; P < 0.001), whereas MR-proADM decreased (from 573 ± 153 to 534 ± 173 pmol/L; P <0.001). Changes (Δ) in MR-proANP correlated with Δfat mass (r = -0.359; P = 0.011) and Δglucose (r = -0.495; P <0.001), while increases in NT-proBNP were primarily associated with reduced plasma glucose (r = -0.462; P <0.001). A modest but significant weight loss of 6% (P < 0.001) was found in the control group with no changes in plasma concentrations of NT-proBNP or MR-proANP, and a minor change in MR-proADM.
Conclusions: Plasma NT-proBNP and MR-proANP concentrations increase and MR-proADM concentration decreases during weight loss, underlining the dynamic impact of BMI, body composition and glucose metabolism on these cardiovascular biomarkers.
Keywords: Body Composition; Hypo-caloric diet; Natriuretic peptides; Obesity; Weight Loss.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between the heart and adipose tissue in cachectic heart failure patients with respect to alterations in body composition: a prospective study.Metabolism. 2014 Jan;63(1):141-9. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.017. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140097
-
Comparison of pleural N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, midregion pro-atrial natriuretic peptide and mid-region pro-adrenomedullin for the diagnosis of pleural effusions associated with cardiac failure.Respirology. 2013 Apr;18(3):540-5. doi: 10.1111/resp.12039. Respirology. 2013. PMID: 23278975
-
Adaptive cardiovascular hormones in a spectrum of heart failure phenotypes.Int J Cardiol. 2015;189:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.03.381. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25885866
-
Biomarkers and diagnostics in heart failure.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2442-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.12.014. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23313577 Review.
-
ProANP and proBNP in plasma as biomarkers of heart failure.Biomark Med. 2019 Sep;13(13):1129-1135. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2019-0158. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Biomark Med. 2019. PMID: 31468978
Cited by
-
Renal and Cardiovascular Effects of SGLT2 Inhibition in Combination With Loop Diuretics in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Heart Failure: The RECEDE-CHF Trial.Circulation. 2020 Nov 3;142(18):1713-1724. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048739. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32865004 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Midregional N-Terminal Pro-Atrial Natriuretic Peptide and Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity 2 Levels on Heart Rhythm in Patients Treated With Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: The Biorhythm Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Jul 6;10(13):e020917. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.020917. Epub 2021 Jun 30. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34187182 Free PMC article.
-
Early Stages of Obesity-related Heart Failure Are Associated with Natriuretic Peptide Deficiency and an Overall Lack of Neurohormonal Activation: The Copenhagen Heart Failure Risk Study.Glob Heart. 2020 Mar 25;15(1):25. doi: 10.5334/gh.776. Glob Heart. 2020. PMID: 32489798 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Circulating Biomarkers of Atrial Fibrillation-Related Pathways among Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: Results from a Randomized Trial.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 7;13(7):2132. doi: 10.3390/jcm13072132. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38610897 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of tirzepatide on circulatory overload and end-organ damage in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and obesity: a secondary analysis of the SUMMIT trial.Nat Med. 2025 Feb;31(2):544-551. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03374-z. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 39551891 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, Stromberg A, van Veldhuisen DJ, Atar D, Hoes AW, Keren A, Mebazaa A, Nieminen M, Priori SG, Swedberg K, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM) Eur Heart J. 2008;29:2388–2442. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehn309. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kistorp C, Raymond I, Pedersen F, Gustafsson F, Faber J, Hildebrandt P. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, C-reactive protein, and urinary albumin levels as predictors of mortality and cardiovascular events in older adults. JAMA. 2005;293:1609–1616. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.13.1609. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maisel A, Mueller C, Nowak R, Peacock WF, Landsberg JW, Ponikowski P, Mockel M, Hogan C, Wu AH, Richards M, Clopton P, Filippatos GS, Di Somma S, Anand I, Ng L, Daniels LB, Neath SX, Christenson R, Potocki M, McCord J, Terracciano G, Kremastinos D, Hartmann O, von Haehling S, Bergmann A, Morgenthaler NG, Anker SD. Mid-region pro-hormone markers for diagnosis and prognosis in acute dyspnea: results from the BACH (Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:2062–2076. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.025. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

