Quantitative hydrophilic interaction chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of N-acetylneuraminic acid and N-acetylmannosamine in human plasma
- PMID: 26218770
- PMCID: PMC4544686
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.07.018
Quantitative hydrophilic interaction chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of N-acetylneuraminic acid and N-acetylmannosamine in human plasma
Abstract
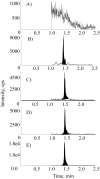
N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac or NANA) is the most predominant sialic acid in mammals. As a terminal component in many glycoproteins and glycolipids, sialic acid is believed to be an important biomarker related to various diseases. Its precursor, N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc), is being investigated as a potential treatment for GNE myopathy. In this work, we developed two highly sensitive and selective liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) methods for the quantitation of ManNAc and free Neu5Ac in human plasma. A fit-for-purpose approach was adopted during method validation and sample analysis. To measure the endogenous compounds and overcome the interference from plasma samples, a surrogate matrix that contained 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used for the preparation of calibration standards and certain levels of quality control (QC) samples. QC samples at higher concentrations were prepared in the authentic matrix (human plasma) to best mimic incurred samples. For both methods, an Ostro 96-well phospholipid removal plate was used for sample extraction, which efficiently removed the phospholipids from the plasma samples prior to LC injection, eliminated matrix effect, and improved sensitivity. Chromatographic separation was achieved using hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) and gradient elution in order to retain the two polar compounds. The lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) for ManNAc and Neu5Ac was 10.0 and 25.0ng/mL, respectively. The overall accuracy of the two assays was within 100%±8.3% based on three levels of QC samples. Inter- and intra-run precision (coefficient of variation (%CV)) across three analytical runs was less than 6.7% for ManNAc and less than 10.8% for Neu5Ac. These methods have been validated to support clinical studies.
Keywords: HILIC; LC–MS/MS; N-acetylmannosamine; N-acetylneuraminic acid; Phospholipid removal; Validation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population Pharmacokinetic Model of N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) and N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) in Subjects with GNE Myopathy.Drugs R D. 2021 Jun;21(2):189-202. doi: 10.1007/s40268-021-00343-6. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Drugs R D. 2021. PMID: 33893973 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitation of cytidine-5'-monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid in human leukocytes using LC-MS/MS: method development and validation.Biomed Chromatogr. 2020 Feb;34(2):e4735. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4735. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Biomed Chromatogr. 2020. PMID: 31691999 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, pharmacokinetics and sialic acid production after oral administration of N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) to subjects with GNE myopathy.Mol Genet Metab. 2017 Sep;122(1-2):126-134. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2017.04.010. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Mol Genet Metab. 2017. PMID: 28641925 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Quantification of free sialic acid in human plasma through a robust quinoxalinone derivatization and LC-MS/MS using isotope-labeled standard calibration.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Jan 1;944:75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.11.016. Epub 2013 Nov 14. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24291723
-
Quantitation of leukotriene B(4) in human sputum as a biomarker using UPLC-MS/MS.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Aug 1;932:59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Jun 20. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23831697
Cited by
-
Impact of Food on the Oral Absorption of N-Acetyl-D-Mannosamine in Healthy Men and Women.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2024 Aug;13(8):876-883. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.1433. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2024. PMID: 38899758 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical and molecular findings in three Japanese patients with N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase-congenital disorder of glycosylation (NANS-CDG).Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 12;12(1):17079. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21751-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36224347 Free PMC article.
-
Internalization of a novel, huge lectin from Ibacus novemdentatus (slipper lobster) induces apoptosis of mammalian cancer cells.Glycoconj J. 2017 Feb;34(1):85-94. doi: 10.1007/s10719-016-9731-x. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Glycoconj J. 2017. PMID: 27658397
-
Analysis of the intramolecular 1,7-lactone of N-acetylneuraminic acid using HPLC-MS: relationship between detection and stability.Glycoconj J. 2023 Jun;40(3):343-354. doi: 10.1007/s10719-023-10114-x. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Glycoconj J. 2023. PMID: 37084126 Free PMC article.
-
Population Pharmacokinetic Model of N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) and N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) in Subjects with GNE Myopathy.Drugs R D. 2021 Jun;21(2):189-202. doi: 10.1007/s40268-021-00343-6. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Drugs R D. 2021. PMID: 33893973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boons G-J, Kamerling JP, Lee YC, Suzuki A, Taniguchi N, Voragen AGJ, editors. Comprehensive glycoscience: from chemistry to systems biology. first Elsevier Ltd.; Oxford, UK: 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

