Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5 in human liposarcomas
- PMID: 26219418
- PMCID: PMC4518222
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12580
Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5 in human liposarcomas
Abstract
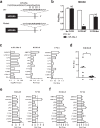
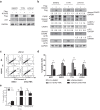
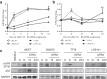
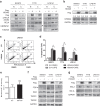
Dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDLPS) is a highly malignant subtype of human liposarcoma (LPS), whose genomic profile is characterized by chromosomal amplification at 12q13-q22. miR-26a-2 is one of the most frequently amplified genes in the region, and inhibition of its downstream target genes likely contributes to LPS tumorigenesis. Our previous study of LPS predicted homeobox protein A5 (HOXA5) as a target of miR-26a-2, and here we explored further the function of HOXA5, and its relationship with miR-26a-2 in DDLPS cells. Compared to normal human adipocytes, all LPS cell lines showed significant downregulation of HOXA5 (p = 0.046), and inhibition of miR-26a-2 using anti-miR-26a-2 substantially upregulated HOXA5 expression in these LPS cells. Interestingly, overexpression of HOXA5 alone induced very strong apoptotic response of LPS cells. HOXA5-induced apoptosis was p53-independent and caspase-dependent. Surprisingly, overexpression of HOXA5 induced nuclear translocation of RELA (p65), which was not associated with the transcriptional activity of RELA. Rather, nucleolar sequestration of RELA was observed. Overall, our study demonstrated for the first time that the downregulation of HOXA5 in LPS cells, partly by overexpression of miR-26a-2 in DDLPS, confers LPS cells resistance to apoptotic death. Further studies are required to understand the relationship of HOXA5 and the NFκB pathway in LPS cells.
Figures

References
-
- Singer S. et al. Gene expression profiling of liposarcoma identifies distinct biological types/subtypes and potential therapeutic targets in well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Cancer Res 67, 6626–6636 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ray-Coquard I. et al. Effect of the MDM2 antagonist RG7112 on the P53 pathway in patients with MDM2-amplified, well-differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma: an exploratory proof-of-mechanism study. Lancet Oncol 13, 1133–1140 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Gesta S., Tseng Y. H. & Kahn C. R. Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell 131, 242–256 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

