Legionella suppresses the host unfolded protein response via multiple mechanisms
- PMID: 26219498
- PMCID: PMC4519984
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8887
Legionella suppresses the host unfolded protein response via multiple mechanisms
Abstract
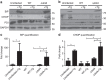
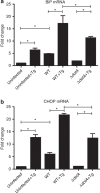
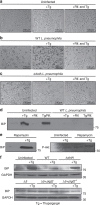
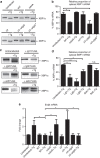
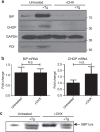
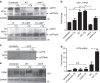
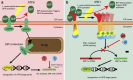
The intracellular pathogen, Legionella pneumophila, secretes ∼300 effector proteins to modulate the host environment. Given the intimate interaction between L. pneumophila and the endoplasmic reticulum, we investigated the role of the host unfolded protein response (UPR) during L. pneumophila infection. Interestingly, we show that the host identifies L. pneumophila infection as a form of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the sensor pATF6 is processed to generate pATF6(N), a transcriptional activator of downstream UPR genes. However, L. pneumophila is able to suppress the UPR and block the translation of prototypical UPR genes, BiP and CHOP. Furthermore, biochemical studies reveal that L. pneumophila uses two effectors (Lgt1 and Lgt2) to inhibit the splicing of XBP1u mRNA to spliced XBP1 (XBP1s), an UPR response regulator. Thus, we demonstrate that L. pneumophila is able to inhibit the UPR by multiple mechanisms including blocking XBP1u splicing and causing translational repression. This observation highlights the utility of L. pneumophila as a powerful tool for studying a critical protein homeostasis regulator.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gene regulatory network of unfolded protein response genes in endoplasmic reticulum stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013 Jan;18(1):11-23. doi: 10.1007/s12192-012-0351-5. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013. PMID: 22802018 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of host cell translation elongation by Legionella pneumophila blocks the host cell unfolded protein response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 8;112(49):E6790-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508716112. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26598709 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical activation of the ER stress sensor ATF6 by Legionella pneumophila effectors.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Oct 11;4(12):e202101247. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101247. Print 2021 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34635501 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella pneumophila type IV effectors hijack the transcription and translation machinery of the host cell.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Dec;24(12):771-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25012125 Review.
-
Emerging roles for XBP1, a sUPeR transcription factor.Gene Expr. 2010;15(1):13-25. doi: 10.3727/105221610x12819686555051. Gene Expr. 2010. PMID: 21061914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Viewing Legionella pneumophila Pathogenesis through an Immunological Lens.J Mol Biol. 2019 Oct 4;431(21):4321-4344. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.028. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31351897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coxiella burnetii Requires Host Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2α Activity for Efficient Intracellular Replication.Infect Immun. 2020 Jun 22;88(7):e00096-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00096-20. Print 2020 Jun 22. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32284364 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Paralogs: The Multiple Layers of Redundancy in Bacterial Pathogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Nov 15;7:467. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00467. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29188194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in Symbiont-Induced Host Cellular Differentiation.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2020;69:137-176. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51849-3_5. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2020. PMID: 33263871 Free PMC article.
-
Arthropods Under Pressure: Stress Responses and Immunity at the Pathogen-Vector Interface.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 15;11:629777. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.629777. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33659000 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vogel J. P., Andrews H. L., Wong S. K. & Isberg R. R. Conjugative transfer by the virulence system of Legionella pneumophila. Science 279, 873–876 (1998) . - PubMed
-
- Mori K. Signalling pathways in the unfolded protein response: development from yeast to mammals. J. Biochem. 146, 743–750 (2009) . - PubMed
-
- Walter P. & Ron D. The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334, 1081–1086 (2011) . - PubMed
-
- Harding H. P., Zhang Y. & Ron D. Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature 397, 271–274 (1999) . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

