Legionella suppresses the host unfolded protein response via multiple mechanisms
- PMID: 26219498
- PMCID: PMC4519984
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8887
Legionella suppresses the host unfolded protein response via multiple mechanisms
Abstract
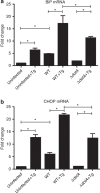
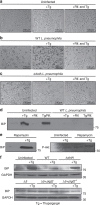
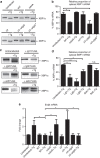
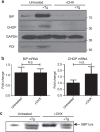
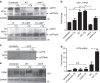
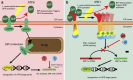
The intracellular pathogen, Legionella pneumophila, secretes ∼300 effector proteins to modulate the host environment. Given the intimate interaction between L. pneumophila and the endoplasmic reticulum, we investigated the role of the host unfolded protein response (UPR) during L. pneumophila infection. Interestingly, we show that the host identifies L. pneumophila infection as a form of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the sensor pATF6 is processed to generate pATF6(N), a transcriptional activator of downstream UPR genes. However, L. pneumophila is able to suppress the UPR and block the translation of prototypical UPR genes, BiP and CHOP. Furthermore, biochemical studies reveal that L. pneumophila uses two effectors (Lgt1 and Lgt2) to inhibit the splicing of XBP1u mRNA to spliced XBP1 (XBP1s), an UPR response regulator. Thus, we demonstrate that L. pneumophila is able to inhibit the UPR by multiple mechanisms including blocking XBP1u splicing and causing translational repression. This observation highlights the utility of L. pneumophila as a powerful tool for studying a critical protein homeostasis regulator.
Figures
References
-
- Vogel J. P., Andrews H. L., Wong S. K. & Isberg R. R. Conjugative transfer by the virulence system of Legionella pneumophila. Science 279, 873–876 (1998) . - PubMed
-
- Mori K. Signalling pathways in the unfolded protein response: development from yeast to mammals. J. Biochem. 146, 743–750 (2009) . - PubMed
-
- Walter P. & Ron D. The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334, 1081–1086 (2011) . - PubMed
-
- Harding H. P., Zhang Y. & Ron D. Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature 397, 271–274 (1999) . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

