Hypoxia accelerates vascular repair of endothelial colony-forming cells on ischemic injury via STAT3-BCL3 axis
- PMID: 26219963
- PMCID: PMC4522108
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-015-0128-8
Hypoxia accelerates vascular repair of endothelial colony-forming cells on ischemic injury via STAT3-BCL3 axis
Abstract
Introduction: Endothelial colony-forming cells (ECFCs) significantly improve tissue repair by providing regeneration potential within injured cardiovascular tissue. However, ECFC transplantation into ischemic tissue exhibits limited therapeutic efficacy due to poor engraftment in vivo. We established an adequate ex vivo expansion protocol and identified novel modulators that enhance functional bioactivities of ECFCs.
Methods: To augment the regenerative potential of ECFCs, functional bioactivities of hypoxia-preconditioned ECFCs (hypo-ECFCs) were examined.
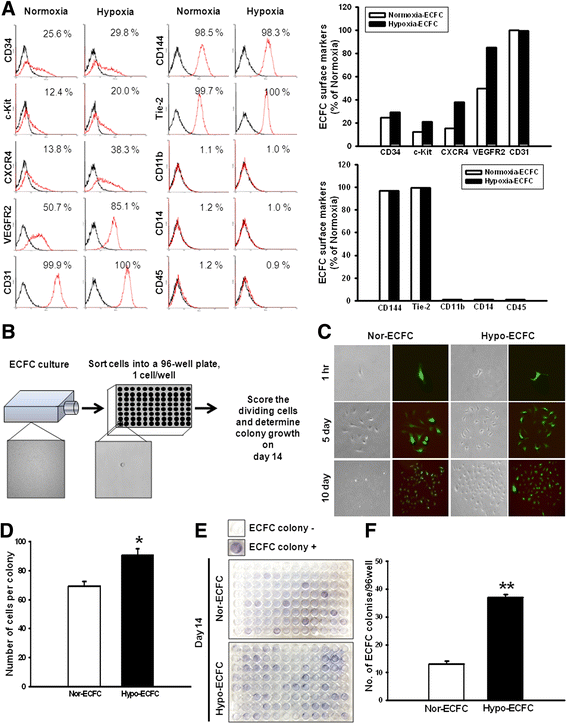
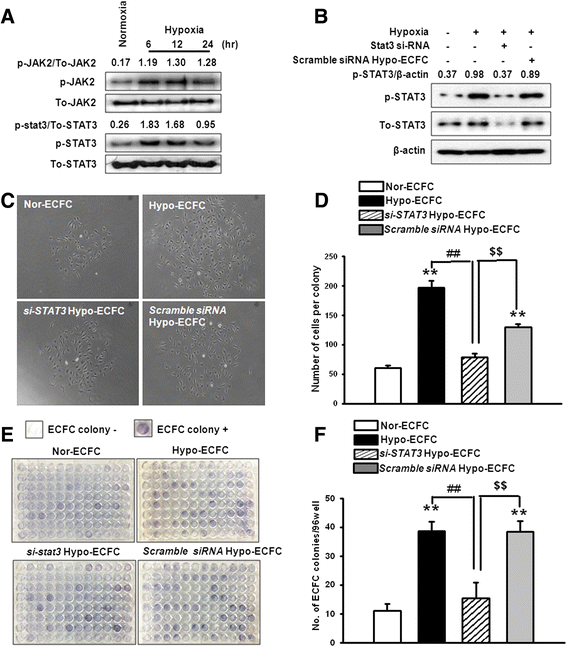
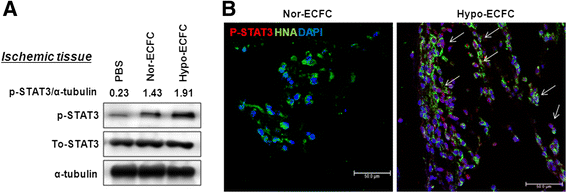
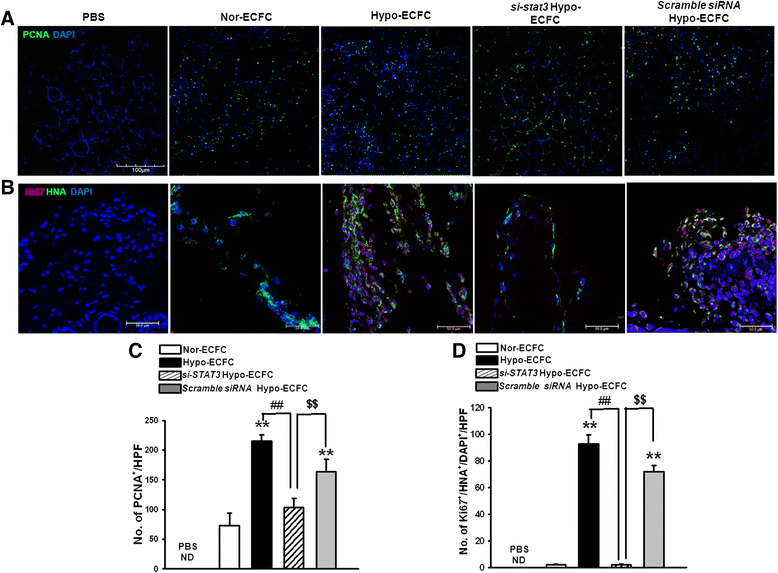
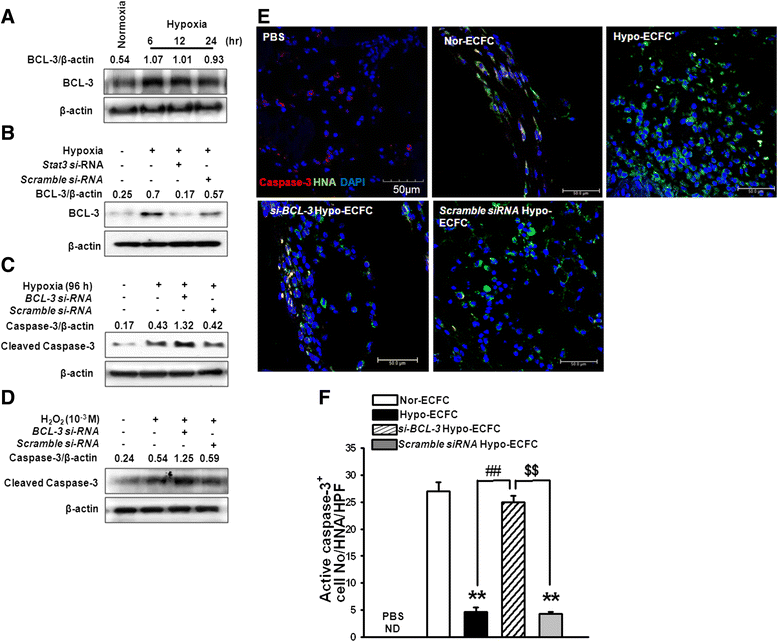
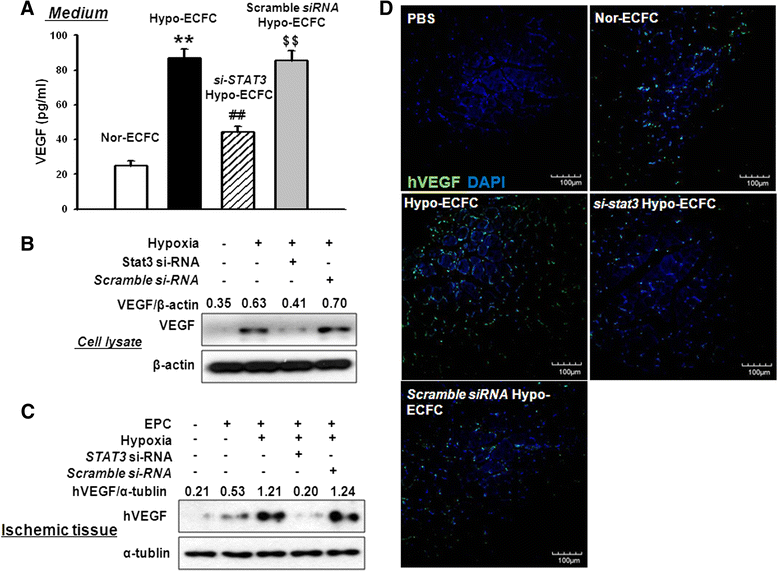
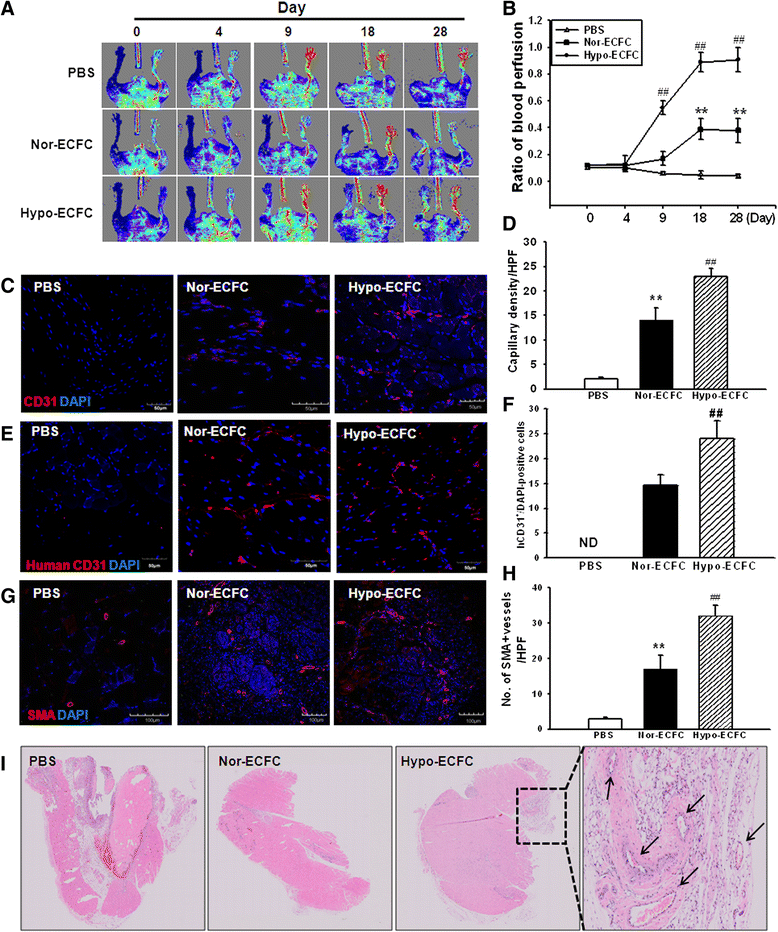
Results: Phosphorylations of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and clonogenic proliferation were enhanced by short-term ECFC culturing under hypoxia, whereas siRNA-targeting of STAT3 significantly reduced these activities. Expression of BCL3, a target molecule of STAT3, was increased in hypo-ECFCs. Moreover, siRNA inhibition of BCL3 markedly reduced survival of ECFCs during hypoxic stress in vitro and ischemic stress in vivo. In a hindlimb ischemia model of ischemia, hypo-ECFC transplantation enhanced blood flow ratio, capillary density, transplanted cell proliferation and survival, and angiogenic cytokine secretion at ischemic sites.
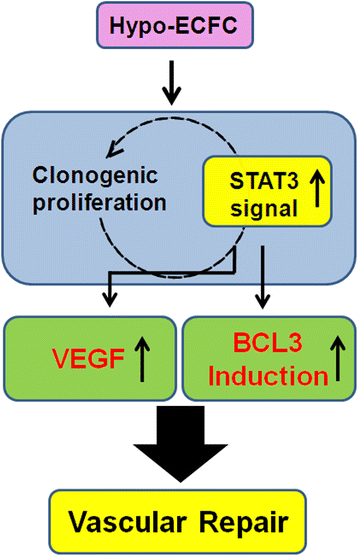
Conclusions: Hypoxia preconditioning facilitates functional bioactivities of ECFCs by mediating regulation of the STAT3-BCL3 axis. Thus, a hypoxic preconditioned ex vivo expansion protocol triggers expansion and functional bioactivities of ECFCs via modulation of the hypoxia-induced STAT3-BCL3 axis, suggesting that hypo-ECFCs offer a therapeutic strategy for accelerated neovasculogenesis in ischemic diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selective Interference Targeting of Lnk in Umbilical Cord-Derived Late Endothelial Progenitor Cells Improves Vascular Repair, Following Hind Limb Ischemic Injury, via Regulation of JAK2/STAT3 Signaling.Stem Cells. 2015 May;33(5):1490-500. doi: 10.1002/stem.1938. Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25537795
-
WKYMVm-induced activation of formyl peptide receptor 2 stimulates ischemic neovasculogenesis by promoting homing of endothelial colony-forming cells.Stem Cells. 2014 Mar;32(3):779-90. doi: 10.1002/stem.1578. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 24155208
-
Hypoxia inhibits cellular senescence to restore the therapeutic potential of old human endothelial progenitor cells via the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-TWIST-p21 axis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Oct;33(10):2407-14. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301931. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23928864
-
Therapeutic Potential of Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells in Ischemic Disease: Strategies to Improve their Regenerative Efficacy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 7;21(19):7406. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197406. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33036489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune-privileged cord blood-derived endothelial colony-forming cells: advancing immunomodulation and vascular regeneration.Angiogenesis. 2025 Mar 6;28(2):19. doi: 10.1007/s10456-025-09973-9. Angiogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40047974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of hypoxia‑mediated cellular prion protein functional change in stem cells and potential application in angiogenesis (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2017 Nov;16(5):5747-5751. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7387. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28901450 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced expression of cellular prion protein improves the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Oct 6;7(10):e2395. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.310. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27711081 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Impairs Initial Outgrowth of Endothelial Colony Forming Cells and Reduces Their Proliferative and Sprouting Potential.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Dec 20;5:356. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00356. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30619865 Free PMC article.
-
Cripto Enhances Proliferation and Survival of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Up-Regulating JAK2/STAT3 Pathway in a GRP78-Dependent Manner.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018 Sep 1;26(5):464-473. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2017.099. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018. PMID: 28835002 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 in tumor angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 4;8(40):69139-69161. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19932. eCollection 2017 Sep 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28978186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

