Identification of siRNA delivery enhancers by a chemical library screen
- PMID: 26220182
- PMCID: PMC4652771
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv762
Identification of siRNA delivery enhancers by a chemical library screen
Abstract
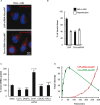
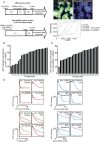
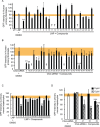
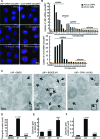
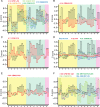
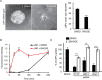
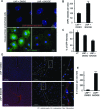
Most delivery systems for small interfering RNA therapeutics depend on endocytosis and release from endo-lysosomal compartments. One approach to improve delivery is to identify small molecules enhancing these steps. It is unclear to what extent such enhancers can be universally applied to different delivery systems and cell types. Here, we performed a compound library screen on two well-established siRNA delivery systems, lipid nanoparticles and cholesterol conjugated-siRNAs. We identified fifty-one enhancers improving gene silencing 2-5 fold. Strikingly, most enhancers displayed specificity for one delivery system only. By a combination of quantitative fluorescence and electron microscopy we found that the enhancers substantially differed in their mechanism of action, increasing either endocytic uptake or release of siRNAs from endosomes. Furthermore, they acted either on the delivery system itself or the cell, by modulating the endocytic system via distinct mechanisms. Interestingly, several compounds displayed activity on different cell types. As proof of principle, we showed that one compound enhanced siRNA delivery in primary endothelial cells in vitro and in the endocardium in the mouse heart. This study suggests that a pharmacological approach can improve the delivery of siRNAs in a system-specific fashion, by exploiting distinct mechanisms and acting upon multiple cell types.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Buyens K., De Smedt S.C., Braeckmans K., Demeester J., Peeters L., van Grunsven L.A., de Mollerat du Jeu X., Sawant R., Torchilin V., Farkasova K., et al. Liposome based systems for systemic siRNA delivery: stability in blood sets the requirements for optimal carrier design. J. Control. Release. 2012;158:362–370. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Davila V., Seifalian A.M., Loizidou M. Organic nanocarriers for cancer drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012;12:414–419. - PubMed
-
- Nair J., Willoughby J., Chan A., Charisse K., Alam R.M., Wang Q., Hoekstra M., Kandasamy P., Kel'in A.V., Milstein S., et al. Multivalent N-Acetylgalactosamine-Conjugated siRNA Localizes in Hepatocytes and Elicits Robust RNAi-mediated Gene Silencing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014;136:16958–16961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

