Vascular permeability--the essentials
- PMID: 26220421
- PMCID: PMC4526869
- DOI: 10.3109/03009734.2015.1064501
Vascular permeability--the essentials
Abstract
The vasculature, composed of vessels of different morphology and function, distributes blood to all tissues and maintains physiological tissue homeostasis. In pathologies, the vasculature is often affected by, and engaged in, the disease process. This may result in excessive formation of new, unstable, and hyperpermeable vessels with poor blood flow, which further promotes hypoxia and disease propagation. Chronic vessel permeability may also facilitate metastatic spread of cancer. Thus, there is a strong incentive to learn more about an important aspect of vessel biology in health and disease: the regulation of vessel permeability. The current review aims to summarize current insights into different mechanisms of vascular permeability, its regulatory factors, and the consequences for disease.
Keywords: Edema; VEGF; histamine; junctions; pore; vascular permeability.
Figures
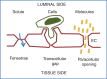


References
-
- Lanitis E, Irving M, Coukos G. Targeting the tumor vasculature to enhance T cell activity . Curr Opin Immunol. 2015;33:55–63. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liao D, Johnson RS. Hypoxia: a key regulator of angiogenesis in cancer . Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:281–90. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. Molecular heterogeneity of tumor endothelium . Cell Tissue Res. 2009;335:271–81. - PubMed
-
- Paolinelli R, Corada M, Orsenigo F, Dejana E. The molecular basis of the blood brain barrier differentiation and maint... . Pharmacol Res. 2011;63:165–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
