MATERNAL EXPERIENCE OF ABUSE IN CHILDHOOD AND DEPRESSIVE SYMPTOMS IN ADOLESCENT AND ADULT OFFSPRING: A 21-YEAR LONGITUDINAL STUDY
- PMID: 26220852
- PMCID: PMC4591211
- DOI: 10.1002/da.22395
MATERNAL EXPERIENCE OF ABUSE IN CHILDHOOD AND DEPRESSIVE SYMPTOMS IN ADOLESCENT AND ADULT OFFSPRING: A 21-YEAR LONGITUDINAL STUDY
Abstract
Background: Intergenerational effects of child abuse have been documented, but it is unknown whether maternal childhood abuse influences offspring mental health in adolescence or adulthood.
Methods: To examine whether maternal experience of childhood abuse is associated with depressive symptoms in adolescent and young adult offspring, we linked data from two large longitudinal cohorts of women (N = 8,882) and their offspring (N = 11,402), and we examined three possible pathways by which maternal experience of abuse might be associated with offspring depressive symptoms: maternal mental health, family characteristics, and offspring's own experience of abuse.
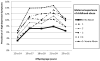
Results: Offspring of women who experienced severe versus no childhood abuse had greater likelihood of high depressive symptoms (RR = 1.78, 95% CI = 1.47, 2.16) and persistent high depressive symptoms (RR = 2.47, 95% CI = 1.37, 4.44). Maternal mental health accounted for 20.9% and offspring's exposure to abuse accounted for 30.3% of the elevated risk of high depressive symptoms. Disparities in offspring depressive symptoms by maternal abuse exposure were evident at age 12 years and persisted through age 31 years.
Conclusions: Findings provide evidence that childhood abuse adversely affects the mental health of the victim's offspring well into adulthood. As offspring exposure to abuse and maternal mental health accounted for more than 50% of the elevated risk of high depressive symptoms among offspring of women who experienced abuse, improving maternal mental health and parenting practices may reduce offspring risk for depressive symptoms in these families.
Keywords: adolescent; adult offspring; child abuse; depression; maternal behavior; sexual abuse.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intergenerational transmission of maltreatment and psychopathology: the role of antenatal depression.Psychol Med. 2013 Mar;43(3):519-28. doi: 10.1017/S0033291712001298. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Psychol Med. 2013. PMID: 22694795 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Childhood Maltreatment and Adolescent Internalizing Problems: The Mediating Role of Maternal Depressive Symptoms and Offspring Childhood Maltreatment.J Youth Adolesc. 2024 Jan;53(1):159-170. doi: 10.1007/s10964-023-01877-5. Epub 2023 Oct 4. J Youth Adolesc. 2024. PMID: 37794285
-
The impact of childhood abuse history, domestic violence and mental health symptoms on parenting behaviour among mothers in Japan.Child Care Health Dev. 2012 Jul;38(4):530-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2214.2011.01272.x. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Child Care Health Dev. 2012. PMID: 21696427
-
Intergenerational Effect of Maternal Childhood Maltreatment on Next Generation's Vulnerability to Psychopathology: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis.Trauma Violence Abuse. 2022 Jan;23(1):152-162. doi: 10.1177/1524838020933870. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2022. PMID: 32588771
-
Intergenerational transmission of depression: clinical observations and molecular mechanisms.Mol Psychiatry. 2019 Aug;24(8):1157-1177. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0265-4. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Mol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30283036 Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship between surrounding greenness in childhood and adolescence and depressive symptoms in adolescence and early adulthood.Ann Epidemiol. 2018 Apr;28(4):213-219. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Ann Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 29426730 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin pathways in the intergenerational transmission of maternal early life stress.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017 Feb;73:293-308. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.12.026. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017. PMID: 28027955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marital transitions during earlier adulthood and subsequent health and well-being in mid- to late-life among female nurses: An outcome-wide analysis.Glob Epidemiol. 2023 Feb 10;5:100099. doi: 10.1016/j.gloepi.2023.100099. eCollection 2023 Dec. Glob Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 37638366 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to childhood abuse is associated with human sperm DNA methylation.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Oct 2;8(1):194. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0252-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30279435 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of childhood trauma on psychological interventions for depression during pregnancy and postpartum: a systematic review.Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021 Jun;24(3):367-380. doi: 10.1007/s00737-020-01066-4. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021. PMID: 33040264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anda RF, Croft JB, Felitti VJ, et al. Adverse childhood experiences and smoking during adolescence and adulthood. JAMA. 1999;282(17):1652–1658. - PubMed
-
- Felitti VJ, Anda RF, Nordenberg D, et al. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults: the adverse childhood experiences (ACE) study. Am JPrev Med. 1998;14(4):245–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

