Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarker in cognitively normal subjects
- PMID: 26220940
- PMCID: PMC4643624
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awv199
Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarker in cognitively normal subjects
Abstract
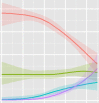
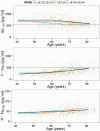
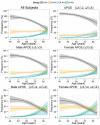
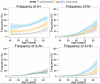
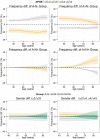
In a large multicentre sample of cognitively normal subjects, as a function of age, gender and APOE genotype, we studied the frequency of abnormal cerebrospinal fluid levels of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers including: total tau, phosphorylated tau and amyloid-β1-42. Fifteen cohorts from 12 different centres with either enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays or Luminex® measurements were selected for this study. Each centre sent nine new cerebrospinal fluid aliquots that were used to measure total tau, phosphorylated tau and amyloid-β1-42 in the Gothenburg laboratory. Seven centres showed a high correlation with the new Gothenburg measurements; therefore, 10 cohorts from these centres are included in the analyses here (1233 healthy control subjects, 40-84 years old). Amyloid-β amyloid status (negative or positive) and neurodegeneration status (negative or positive) was established based on the pathological cerebrospinal fluid Alzheimer's disease cut-off values for cerebrospinal fluid amyloid-β1-42 and total tau, respectively. While gender did not affect these biomarker values, APOE genotype modified the age-associated changes in cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers such that APOE ε4 carriers showed stronger age-related changes in cerebrospinal fluid phosphorylated tau, total tau and amyloid-β1-42 values and APOE ε2 carriers showed the opposite effect. At 40 years of age, 76% of the subjects were classified as amyloid negative, neurodegeneration negative and their frequency decreased to 32% at 85 years. The amyloid-positive neurodegeneration-negative group remained stable. The amyloid-negative neurodegeneration-positive group frequency increased slowly from 1% at 44 years to 16% at 85 years, but its frequency was not affected by APOE genotype. The amyloid-positive neurodegeneration-positive frequency increased from 1% at 53 years to 28% at 85 years. Abnormally low cerebrospinal fluid amyloid-β1-42 levels were already frequent in midlife and APOE genotype strongly affects the levels of cerebrospinal fluid amyloid-β1-42, phosphorylated tau and total tau across the lifespan without influencing the frequency of subjects with suspected non-amyloid pathology.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biomarkers; cognitive ageing; dementia; imaging.
© The Author (2015). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Berenguer RG, Monge Argiles JA, Ruiz CM, Paya JS, Blanco Canto MA, Santana CL. Alzheimer disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers predict cognitive decline in healthy elderly over 2 years. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2014; 28: 234–8. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Del Tredici K. The pathological process underlying Alzheimer's disease in individuals under thirty. Acta Neuropathol 2011; 121: 171–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG022374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG036694/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- P50 NS053488/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG1210/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG022374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG13616/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG042856/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118624/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG033655/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG043885/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG032953/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

