Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Lewy Body Disorders: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26221005
- PMCID: PMC4772820
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv086
Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Lewy Body Disorders: A Meta-Analysis
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Apr 27;19(10):pyw031. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw031. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27207904 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: We performed a meta-analysis of cholinesterase inhibitors for patients with Lewy body disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, Parkinson's disease dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies.
Methods: The meta-analysis included only randomized controlled trials of cholinesterase inhibitors for Lewy body disorders.
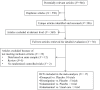
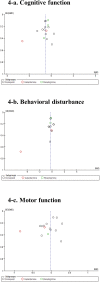
Results: Seventeen studies (n = 1798) were assessed. Cholinesterase inhibitors significantly improved cognitive function (standardized mean difference [SMD] = -0.53], behavioral disturbances (SMD = -0.28), activities of daily living (SMD = -0.28), and global function (SMD = -0.52) compared with control treatments. Changes in motor function were not significantly different from control treatments. Furthermore, the cholinesterase inhibitor group had a higher all-cause discontinuation (risk ratio [RR] = 1.48, number needed to harm [NNH] = 14), discontinuation due to adverse events (RR = 1.59, NNH = 20), at least one adverse event (RR = 1.13, NNH = 11), nausea (RR = 2.50, NNH = 13), and tremor (RR = 2.30, NNH = 20).
Conclusions: Cholinesterase inhibitors appear beneficial for the treatment of Lewy body disorders without detrimental effects on motor function. However, a careful monitoring of treatment compliance and side effects is required.
Keywords: Lewy body disorders; Parkinson’s disease; cholinesterase inhibitors; dementia with Lewy bodies; meta-analysis.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures




References
-
- Beversdorf DQ, Warner JL, Davis RA, Sharma UK, Nagaraja HN, Scharre DW. (2004) Donepezil in the treatment of dementia with lewy bodies. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 12:542–544. - PubMed
-
- Boada M, Arranz FJ. (2013) Transdermal is better than oral: observational research of the satisfaction of caregivers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease treated with rivastigmine. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 35:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Bohnen NI, Kaufer DI, Ivanco LS, Lopresti B, Koeppe RA, Davis JG, Mathis CA, Moore RY, DeKosky ST. (2003) Cortical cholinergic function is more severely affected in parkinsonian dementia than in Alzheimer disease: an in vivo positron emission tomographic study. Arch Neurol 60:1745–1748. - PubMed
-
- Candy JM, Perry RH, Perry EK, Irving D, Blessed G, Fairbairn AF, Tomlinson BE. (1983) Pathological changes in the nucleus of Meynert in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. J Neurol Sci 59:277–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

