Modulation of inflammation by autophagy: Consequences for human disease
- PMID: 26222012
- PMCID: PMC4836004
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1071759
Modulation of inflammation by autophagy: Consequences for human disease
Abstract
Autophagy and inflammation are 2 fundamental biological processes involved in both physiological and pathological conditions. Through its crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, autophagy is involved in modulation of cell metabolism, cell survival, and host defense. Defective autophagy is associated with pathological conditions such as cancer, autoimmune disease, neurodegenerative disease, and senescence. Inflammation represents a crucial line of defense against microorganisms and other pathogens, and there is increasing evidence that autophagy has important effects on the induction and modulation of the inflammatory reaction; understanding the balance between these 2 processes may point to important possibilities for therapeutic targeting. This review focuses on the crosstalk between autophagy and inflammation as an emerging field with major implications for understanding the host defense on the one hand, and for the pathogenesis and treatment of immune-mediated diseases on the other hand.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; autoinflammatory diseases; autophagy; carcinogenesis; infectious diseases; inflammation.
Figures
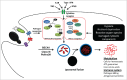

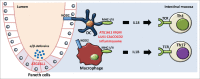

References
-
- Yang Z, Klionsky DJ. Eaten alive: a history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12:814-22; PMID:20811353; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/ncb0910-814 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuballa P, Nolte WM, Castoreno AB, Xavier RJ. Autophagy and the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 2012; 30:611-46; PMID:22449030; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-074948 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deretic V, Saitoh T, Akira S. Autophagy in infection, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13:722-37; PMID:24064518; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nri3532 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heath RJ, Xavier RJ. Autophagy, immunity and human disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2009; 25:512-20; PMID:19826372; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1097/MOG.0b013e32833104f1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y. The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2011; 27:107-32; PMID:21801009; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
