Robustness of Next Generation Sequencing on Older Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue
- PMID: 26222067
- PMCID: PMC4519244
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127353
Robustness of Next Generation Sequencing on Older Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue
Abstract
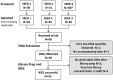
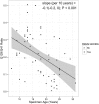
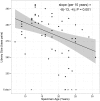
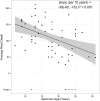
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) technologies are used to detect somatic mutations in tumors and study germ line variation. Most NGS studies use DNA isolated from whole blood or fresh frozen tissue. However, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues are one of the most widely available clinical specimens. Their potential utility as a source of DNA for NGS would greatly enhance population-based cancer studies. While preliminary studies suggest FFPE tissue may be used for NGS, the feasibility of using archived FFPE specimens in population based studies and the effect of storage time on these specimens needs to be determined. We conducted a study to determine whether DNA in archived FFPE high-grade ovarian serous adenocarcinomas from Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) registries Residual Tissue Repositories (RTR) was present in sufficient quantity and quality for NGS assays. Fifty-nine FFPE tissues, stored from 3 to 32 years, were obtained from three SEER RTR sites. DNA was extracted, quantified, quality assessed, and subjected to whole exome sequencing (WES). Following DNA extraction, 58 of 59 specimens (98%) yielded DNA and moved on to the library generation step followed by WES. Specimens stored for longer periods of time had significantly lower coverage of the target region (6% lower per 10 years, 95% CI: 3-10%) and lower average read depth (40x lower per 10 years, 95% CI: 18-60), although sufficient quality and quantity of WES data was obtained for data mining. Overall, 90% (53/59) of specimens provided usable NGS data regardless of storage time. This feasibility study demonstrates FFPE specimens acquired from SEER registries after varying lengths of storage time and under varying storage conditions are a promising source of DNA for NGS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Berg JS, Amendola LM, Eng C, Van Allen E, Gray SW, Wagle N, et al. (2013) Processes and preliminary outputs for identification of actionable genes as incidental findings in genomic sequence data in the Clinical Sequencing Exploratory Research Consortium. Genet Med 15: 860–867. 10.1038/gim.2013.133 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corless CL, Spellman PT (2012) Tackling formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor tissue with next-generation sequencing. Cancer Discov 2: 23–24. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0319 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U58DP000807-3/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- P30 CA086862/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035137/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA071789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC-35143/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC-35137/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035143/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U58 DP000807/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- N01-PC-2010-00035/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

