Cutting Edge: cGAS Is Required for Lethal Autoimmune Disease in the Trex1-Deficient Mouse Model of Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome
- PMID: 26223655
- PMCID: PMC4546858
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500969
Cutting Edge: cGAS Is Required for Lethal Autoimmune Disease in the Trex1-Deficient Mouse Model of Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome
Abstract
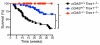
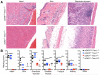
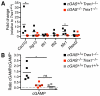
Detection of intracellular DNA triggers activation of the stimulator of IFN genes-dependent IFN-stimulatory DNA (ISD) pathway, which is essential for antiviral immune responses. However, chronic activation of this pathway is implicated in autoimmunity. Mutations in TREX1, a 3' repair exonuclease that degrades cytosolic DNA, cause Aicardi-Goutières syndrome and chilblain lupus. Trex1 (-/-) mice develop lethal, IFN-driven autoimmune disease that is dependent on activation of the ISD pathway, but the DNA sensors that detect the endogenous DNA that accumulates in Trex1 (-/-) mice have not been defined. Multiple DNA sensors have been proposed to activate the ISD pathway, including cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS). In this study, we show that Trex1 (-/-) mice lacking cGAS are completely protected from lethality, exhibit dramatically reduced tissue inflammation, and fail to develop autoantibodies. These findings implicate cGAS as a key driver of autoimmune disease and suggest that cGAS inhibitors may be useful therapeutics for Aicardi-Goutières syndrome and related autoimmune diseases.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Wu J, Chen ZJ. Innate immune sensing and signaling of cytosolic nucleic acids. Annu Rev Immunol. 2014;32:461–488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

