All-Carbon [3+3] Oxidative Annulations of 1,3-Enynes by Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed C-H Functionalization and 1,4-Migration
- PMID: 26224377
- PMCID: PMC4557058
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201503978
All-Carbon [3+3] Oxidative Annulations of 1,3-Enynes by Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed C-H Functionalization and 1,4-Migration
Abstract
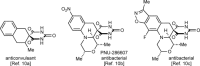
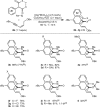
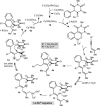
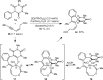
1,3-Enynes containing allylic hydrogens cis to the alkyne function as three-carbon components in rhodium(III)-catalyzed, all-carbon [3+3] oxidative annulations to produce spirodialins. The proposed mechanism of these reactions involves the alkenyl-to-allyl 1,4-rhodium(III) migration.
Keywords: CH activation; allylation; enynes; homogeneous catalysis; rhodium.
© 2015 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figures


Similar articles
-
One-Carbon Oxidative Annulations of 1,3-Enynes by Catalytic C-H Functionalization and 1,4-Rhodium(III) Migration.Chemistry. 2018 Mar 15;24(16):4050-4054. doi: 10.1002/chem.201706043. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29356188
-
Catalytic 1,4-rhodium(III) migration enables 1,3-enynes to function as one-carbon oxidative annulation partners in C-H functionalizations.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014 Sep 8;53(37):9931-5. doi: 10.1002/anie.201406072. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014. PMID: 25048465 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Asymmetric [4+1] and [5+1] Annulation of Arenes and 1,3-Enynes: A Distinct Mechanism of Allyl Formation and Allyl Functionalization.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Dec 7;59(50):22706-22713. doi: 10.1002/anie.202010832. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32886841
-
Asymmetric Rhodium-Catalyzed Allylic Substitution Reactions: Discovery, Development and Applications to Target-Directed Synthesis.J Org Chem. 2018 Oct 5;83(19):11463-11479. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b00583. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Org Chem. 2018. PMID: 30183287 Review.
-
Cobalt- and rhodium-catalyzed carboxylation using carbon dioxide as the C1 source.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2018 Sep 19;14:2435-2460. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.14.221. eCollection 2018. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2018. PMID: 30344768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advancements in the Cyclization Strategies of 1,3-Enynes Towards the Synthesis of Heterocyclic/Carbocyclic Frameworks.Chem Asian J. 2025 Apr 17;20(8):e202401657. doi: 10.1002/asia.202401657. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Chem Asian J. 2025. PMID: 39976556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regioselective Radical Cascade Cyclizations of Alkyne-Tethered Cyclohexadienones with Chalcogenides under Visible-Light Catalysis.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 20;8(39):35809-35821. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03362. eCollection 2023 Oct 3. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37810637 Free PMC article.
-
Arylative Intramolecular Allylation of Ketones with 1,3-Enynes Enabled by Catalytic Alkenyl-to-Allyl 1,4-Rhodium(I) Migration.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017 Jun 12;56(25):7227-7232. doi: 10.1002/anie.201703155. Epub 2017 May 19. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017. PMID: 28523779 Free PMC article.
-
Palladium-catalyzed selective C-C bond cleavage and stereoselective alkenylation between cyclopropanol and 1,3-diyne: one-step synthesis of diverse conjugated enynes.Chem Sci. 2022 Feb 8;13(9):2692-2700. doi: 10.1039/d1sc04780a. eCollection 2022 Mar 2. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35340856 Free PMC article.
-
Hypervalent iodine promoted the synthesis of cycloheptatrienes and cyclopropanes.Chem Sci. 2021 Dec 8;13(2):478-485. doi: 10.1039/d1sc05429e. eCollection 2022 Jan 5. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 35126980 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

