Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in neurons of trigeminal ganglion contributes to nociception induced by acute pulpitis in rats
- PMID: 26224622
- PMCID: PMC4519790
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12549
Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in neurons of trigeminal ganglion contributes to nociception induced by acute pulpitis in rats
Abstract
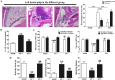
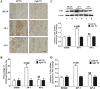
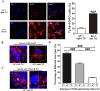
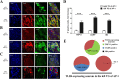
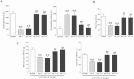
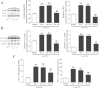
Pain caused by acute pulpitis (AP) is a common symptom in clinical settings. However, its underlying mechanisms have largely remained unknown. Using AP model, we demonstrated that dental injury caused severe pulp inflammation with up-regulated serum IL-1β. Assessment from head-withdrawal reflex thresholds (HWTs) and open-field test demonstrated nociceptive response at 1 day post injury. A consistent up-regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in the trigeminal ganglion (TG) ipsilateral to the injured pulp was found; and downstream signaling components of TLR4, including MyD88, TRIF and NF-κB, and cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β, were also increased. Retrograde labeling indicated that most TLR4 positve neuron in the TG innnervated the pulp and TLR4 immunoreactivity was mainly in the medium and small neurons. Double labeling showed that the TLR4 expressing neurons in the ipsilateral TG were TRPV1 and CGRP positive, but IB4 negative. Furthermore, blocking TLR4 by eritoran (TLR4 antagonist) in TGs of the AP model significantly down-regulated MyD88, TRIF, NF-κB, TNF-α and IL-1β production and behavior of nociceptive response. Our findings suggest that TLR4 signaling in TG cells, particularly the peptidergic TRPV1 neurons, plays a key role in AP-induced nociception, and indicate that TLR4 signaling could be a potential therapeutic target for orofacial pain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of macrophage-mediated Toll-like receptor 4-interleukin-1R signaling in ectopic tongue pain associated with tooth pulp inflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Oct 21;17(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01995-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 33081813 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal toll-like receptor 4-mediated signalling pathway contributes to visceral hypersensitivity induced by neonatal colonic irritation in rats.Eur J Pain. 2015 Feb;19(2):176-86. doi: 10.1002/ejp.534. Epub 2014 May 19. Eur J Pain. 2015. PMID: 24842692
-
[Alveolar macrophage TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway contributes to ventilator-induced lung injury in rats].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Feb;31(2):182-5, 189. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25652858 Chinese.
-
The role of NF-kappaB in the inflammatory processes related to dental caries, pulpitis, apical periodontitis, and periodontitis-a narrative review.PeerJ. 2024 Aug 29;12:e17953. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17953. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39221277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphological foundations of pain processing in dental pulp.J Oral Sci. 2020;62(2):126-130. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.19-0451. J Oral Sci. 2020. PMID: 32224566 Review.
Cited by
-
Heme Causes Pain in Sickle Mice via Toll-Like Receptor 4-Mediated Reactive Oxygen Species- and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Glial Activation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021 Feb 1;34(4):279-293. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7913. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021. PMID: 32729340 Free PMC article.
-
Tuina for peripherally-induced neuropathic pain: A review of analgesic mechanism.Front Neurosci. 2022 Dec 22;16:1096734. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1096734. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36620462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 alleviates hyperalgesia induced by acute dural inflammation in experimental migraine.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806918754612. doi: 10.1177/1744806918754612. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 29310498 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenic inflammation and its role in migraine.Semin Immunopathol. 2018 May;40(3):301-314. doi: 10.1007/s00281-018-0676-y. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Semin Immunopathol. 2018. PMID: 29568973 Review.
-
Inhibition of carrageenan-induced dental inflammatory responses owing to decreased TRPV1 activity by Dexmedetomidine.J Inflamm (Lond). 2020 May 1;17:18. doi: 10.1186/s12950-020-00245-5. eCollection 2020. J Inflamm (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32377171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leeson R. in Endodontics 4th edn (ed. Ng K.) 369–373 (Mosby, 2014).
-
- Byers M. R. & Narhi M. V. Dental injury models: experimental tools for understanding neuroinflammatory interactions and polymodal nociceptor functions. Crit Rev Oral Biol M. 10, 4–39 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Ertekin C., Secil Y., Yuceyar N. & Aydogdu I. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Clin Neurol Neurosur. 10, 32–37 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Bender I. B. Pulpal pain diagnosis–a review. J. Endodont. 26, 175–179 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Farella M., Michelotti A., Gargano A., Cimino R. & Ramaglia L. Myofascial pain syndrome misdiagnosed as odontogenic pain: a case report. Cranio. 20, 307–311 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

