NBCe1 expression is required for normal renal ammonia metabolism
- PMID: 26224717
- PMCID: PMC4593816
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00219.2015
NBCe1 expression is required for normal renal ammonia metabolism
Abstract
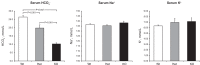
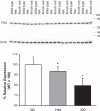
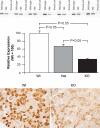
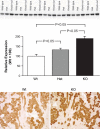
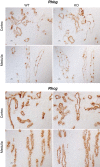
The mechanisms regulating proximal tubule ammonia metabolism are incompletely understood. The present study addressed the role of the proximal tubule basolateral electrogenic Na(+)-coupled bicarbonate cotransporter (NBCe1; Slc4a4) in renal ammonia metabolism. We used mice with heterozygous and homozygous NBCe1 gene deletion and compared these mice with their wild-type littermates. Because homozygous NBCe1 gene deletion causes 100% mortality before day 25, we studied mice at day 8 (±1 day). Both heterozygous and homozygous gene deletion caused a gene dose-related decrease in serum bicarbonate. The ability to lower urinary pH was intact, and even accentuated, with NBCe1 deletion. However, in contrast to the well-known effect of metabolic acidosis to increase urinary ammonia excretion, NBCe1 deletion caused a gene dose-related decrease in ammonia excretion. There was no identifiable change in proximal tubule structure by light microscopy. Examination of proteins involved in renal ammonia metabolism showed decreased expression of phosphate-dependent glutaminase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, key enzymes in proximal tubule ammonia generation, and increased expression of glutamine synthetase, which recycles intrarenal ammonia and regenerates glutamine. Expression of key proteins involved in ammonia transport outside of the proximal tubule (rhesus B glycoprotein and rhesus C glycoprotein) was not significantly changed by NBCe1 deletion. We conclude from these findings that NBCe1 expression is necessary for normal proximal tubule ammonia metabolism.
Keywords: acid-base; ammonia; electrogenic sodium-coupled bicarbonate cotransporter 1; proximal tubule.
Figures



References
-
- Aalkjaer C, Frische S, Leipziger J, Nielsen S, Praetorius J. Sodium coupled bicarbonate transporters in the kidney, an update. Acta Physiol Scand 181: 505–512, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Ambuhl PM, Amemiya M, Danczkay M, Lotscher M, Kaissling B, Moe OW, Preisig PA, Alpern RJ. Chronic metabolic acidosis increases NHE3 protein abundance in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 271: F917–F925, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Baum M, Biemesderfer D, Gentry D, Aronson PS. Ontogeny of rabbit renal cortical NHE3 and NHE1: effect of glucocorticoids. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 268: F815–F820, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Benchimol C, Zavilowitz B, Satlin LM. Developmental expression of ROMK mRNA in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Pediatr Res 47: 46–52, 2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

