Constitutive Expression of Rice MicroRNA528 Alters Plant Development and Enhances Tolerance to Salinity Stress and Nitrogen Starvation in Creeping Bentgrass
- PMID: 26224802
- PMCID: PMC4577425
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.00899
Constitutive Expression of Rice MicroRNA528 Alters Plant Development and Enhances Tolerance to Salinity Stress and Nitrogen Starvation in Creeping Bentgrass
Abstract
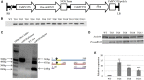
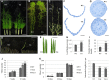
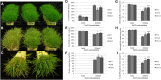
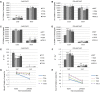
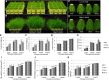
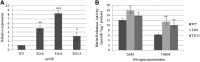
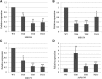
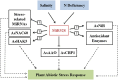
MicroRNA528 (miR528) is a conserved monocot-specific small RNA that has the potential of mediating multiple stress responses. So far, however, experimental functional studies of miR528 are lacking. Here, we report that overexpression of a rice (Oryza sativa) miR528 (Osa-miR528) in transgenic creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera) alters plant development and improves plant salt stress and nitrogen (N) deficiency tolerance. Morphologically, miR528-overexpressing transgenic plants display shortened internodes, increased tiller number, and upright growth. Improved salt stress resistance is associated with increased water retention, cell membrane integrity, chlorophyll content, capacity for maintaining potassium homeostasis, CATALASE activity, and reduced ASCORBIC ACID OXIDASE (AAO) activity; while enhanced tolerance to N deficiency is associated with increased biomass, total N accumulation and chlorophyll synthesis, nitrite reductase activity, and reduced AAO activity. In addition, AsAAO and COPPER ION BINDING PROTEIN1 are identified as two putative targets of miR528 in creeping bentgrass. Both of them respond to salinity and N starvation and are significantly down-regulated in miR528-overexpressing transgenics. Our data establish a key role that miR528 plays in modulating plant growth and development and in the plant response to salinity and N deficiency and indicate the potential of manipulating miR528 in improving plant abiotic stress resistance.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
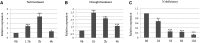
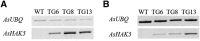


References
-
- Abràmoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton Int 11: 36–43
-
- Abrol Y, Raghuram N (2007) Agricultural Nitrogen Use and Its Environmental Implications. I.K. International Publishing House, New Dehli, India
-
- Ali Y, Aslam Z, Ashraf M, Tahir G (2004) Effect of salinity on chlorophyll concentration, leaf area, yield and yield components of rice genotypes grown under saline environment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1: 221–225
-
- Ashraf M, Foolad M (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59: 206–216
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

