Randomised Comparative Study on Propofol and Diazepam as a Sedating Agent in Day Care Surgery
- PMID: 26225032
- PMCID: PMC4518785
- DOI: 10.1007/s12663-013-0537-0
Randomised Comparative Study on Propofol and Diazepam as a Sedating Agent in Day Care Surgery
Abstract
Objective: The study was conducted to assess the usefulness by qualitative comparison between the two intravenous sedative drugs, Diazepam and Propofol and to provide sedation in apprehensive and uncooperative patients undergoing day care oral surgical procedures.
Methods: The present study was conducted on 20 adult patients, 10 in each group (Propofol and Diazepam) irrespective of age and sex. Intravenous sedation of Propofol compared with Diazepam in terms of onset of action, recovery, and anterograde amnesia, patient co-operation, surgeon's convenience and side effects and other parameters.
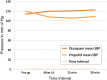
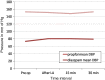
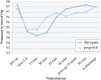
Results: Propofol was found to be the superior sedating agent compared to Diazepam, having rapid onset and predictability of action, profoundness of amnesia and a faster recovery period, offering advantages of early patient discharge and better patient compliance.
Conclusion: Propofol was found to be an ideal sedating agent in day care oral surgical procedures.
Keywords: Diazepam; Propofol; Sedation.
Figures
References
-
- Sarasin DS, Ghoneim NM (1996) Effect of sedation with midazolam or propofol on cognition and psychomotor functions. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 54:1187–1193 - PubMed
-
- White Paul F. Propofol pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics. Semin Anesth. 1988;7:4–20.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources