Endoscopic Resection of Vestibular Schwannomas
- PMID: 26225307
- PMCID: PMC4433394
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1543974
Endoscopic Resection of Vestibular Schwannomas
Abstract
Objective To report our results and the technical details of fully endoscopic resection of vestibular schwannomas. Design Prospective observational study. Setting A single academic institution involving neurosurgery and neurotology. Participants Twelve consecutive patients who underwent fully endoscopic resection of a vestibular schwannoma. Main Outcome Measures Hearing preservation, based on the American Association of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgeons (AAO-HNS) score as well as the Gardener and Robertson Modified Hearing Classification (GR). Facial nerve preservation based on the House-Brackmann (HB) score. Results All patients successfully underwent gross total resection. Facial nerve preservation rate was 92% with 11 of 12 patients retaining an HB score of 1/6 postoperatively. Hearing preservation rate was 67% with 8 of 12 patients maintaining a stable AAO-HNS grade and GR score at follow-up. Mean tumor size was 1.5 cm (range: 1-2 cm). No patients experienced postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leak, infection, or cranial nerve palsy for a complication rate of 0%. Mean operative time was 261.6 minutes with an estimated blood loss of 56.3 mL and average length of hospital stay of 3.6 days. Conclusion A purely endoscopic approach is a safe and effective option for hearing preservation surgery for vestibular schwannomas in appropriately selected patients.
Keywords: acoustic neuroma; cerebellopontine angle; endoscopy; skull base; vestibular schwannoma.
Figures


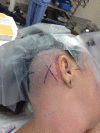
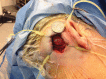

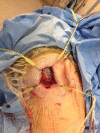
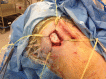

References
-
- Mouton W G, Bessell J R, Maddern G J. Looking back to the advent of modern endoscopy: 150th birthday of Maximilian Nitze. World J Surg. 1998;22(12):1256–1258. - PubMed
-
- Doyen E. Vol 1. London, England: Balliere, Tindall, and Cox; 1917. Surgical Therapeutics and Operative Techniques; pp. 599–602.
-
- Borucki L, Szyfter W, Leszczyńska M. Microscopy and endoscopy of the cerebellopontine angle in the retrosigmoid approach [in Polish] Otolaryngol Pol. 2004;58(3):509–515. - PubMed
-
- Cappabianca P, Cavallo L M, Esposito F, de Divitiis E, Tschabitscher M. Endoscopic examination of the cerebellar pontine angle. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2002;104(4):387–391. - PubMed
-
- Magnan J, Chays A, Lepetre C, Pencroffi E, Locatelli P. Surgical perspectives of endoscopy of the cerebellopontine angle. Am J Otol. 1994;15(3):366–370. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

