The Crosstalk between Nrf2 and TGF-β1 in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Pancreatic Duct Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 26226105
- PMCID: PMC4520686
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132978
The Crosstalk between Nrf2 and TGF-β1 in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Pancreatic Duct Epithelial Cells
Abstract
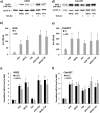
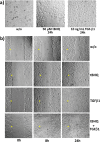
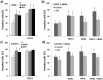
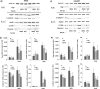
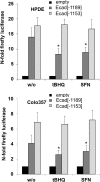
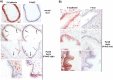
Nrf2 and TGF-β1 both affect tumorigenesis in a dual fashion, either by preventing carcinogen induced carcinogenesis and suppressing tumor growth, respectively, or by conferring cytoprotection and invasiveness to tumor cells during malignant transformation. Given the involvement of Nrf2 and TGF-β1 in the adaptation of epithelial cells to persistent inflammatory stress, e.g. of the pancreatic duct epithelium during chronic pancreatitis, a crosstalk between Nrf2 and TGF-β1 can be envisaged. By using premalignant human pancreatic duct cells (HPDE) and the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell line Colo357, we could show that Nrf2 and TGF-β1 independently but additively conferred an invasive phenotype to HPDE cells, whereas acting synergistically in Colo357 cells. This was accompanied by differential regulation of EMT markers like vimentin, Slug, L1CAM and E-cadherin. Nrf2 activation suppressed E-cadherin expression through an as yet unidentified ARE related site in the E-cadherin promoter, attenuated TGF-β1 induced Smad2/3-activity and enhanced JNK-signaling. In Colo357 cells, TGF-β1 itself was capable of inducing Nrf2 whereas in HPDE cells TGF-β1 per-se did not affect Nrf2 activity, but enhanced Nrf2 induction by tBHQ. In Colo357, but not in HPDE cells, the effects of TGF-β1 on invasion were sensitive to Nrf2 knock-down. In both cell lines, E-cadherin re-expression inhibited the proinvasive effect of Nrf2. Thus, the increased invasion of both cell lines relates to the Nrf2-dependent downregulation of E-cadherin expression. In line, immunohistochemistry analysis of human pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias in pancreatic tissues from chronic pancreatitis patients revealed strong Nrf2 activity already in premalignant epithelial duct cells, accompanied by partial loss of E-cadherin expression. Our findings indicate that Nrf2 and TGF-β1 both contribute to malignant transformation through distinct EMT related mechanisms accounting for an invasive phenotype. Provided a crosstalk between both pathways, Nrf2 and TGF-β1 mutually promote their tumorigenic potential, a condition manifesting already at an early stage during inflammation induced carcinogenesis of the pancreas.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The anti-oxidative transcription factor Nuclear factor E2 related factor-2 (Nrf2) counteracts TGF-β1 mediated growth inhibition of pancreatic ductal epithelial cells -Nrf2 as determinant of pro-tumorigenic functions of TGF-β1.BMC Cancer. 2016 Feb 25;16:155. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2191-7. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26915435 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of L1CAM in pancreatic duct cells is transforming growth factor beta1- and slug-dependent: role in malignant transformation of pancreatic cancer.Cancer Res. 2009 May 15;69(10):4517-26. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3493. Epub 2009 May 12. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19435915
-
The antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 modulates the stress response and phenotype of malignant as well as premalignant pancreatic ductal epithelial cells by inducing expression of the ATF3 splicing variant ΔZip2.Oncogene. 2019 Feb;38(9):1461-1476. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0518-3. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30302023
-
ROS-Nrf2 pathway mediates the development of TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the activation of Notch signaling.Eur J Cell Biol. 2021 Sep-Nov;100(7-8):151181. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2021.151181. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Eur J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34763128 Review.
-
E-Cadherin in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Multifaceted Actor during EMT.Cells. 2020 Apr 22;9(4):1040. doi: 10.3390/cells9041040. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32331358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TGFβ-induced metabolic reprogramming during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Jun;77(11):2103-2123. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03398-6. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31822964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical Profiles and Anticancer Effects of Calophyllum inophyllum L. Extract Relating to Reactive Oxygen Species Modulation on Patient-Derived Cells from Breast and Lung Cancers.Scientifica (Cairo). 2023 Jul 20;2023:6613670. doi: 10.1155/2023/6613670. eCollection 2023. Scientifica (Cairo). 2023. PMID: 37520043 Free PMC article.
-
Salvianolic acid B protects against acute and chronic liver injury by inhibiting Smad2C/L phosphorylation.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Apr;21(4):341. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9772. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33732314 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted role of NRF2 in cancer progression and cancer stem cells maintenance.Arch Pharm Res. 2021 Mar;44(3):263-280. doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01316-8. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Arch Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 33754307 Review.
-
The molecular biology and therapeutic potential of Nrf2 in leukemia.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Jul 29;22(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02660-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35906617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

