Inflammatory targets of therapy in sickle cell disease
- PMID: 26226206
- PMCID: PMC4684475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2015.07.001
Inflammatory targets of therapy in sickle cell disease
Abstract
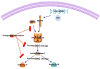
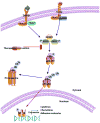
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a monogenic globin disorder characterized by the production of a structurally abnormal hemoglobin (Hb) variant Hb S, which causes severe hemolytic anemia, episodic painful vaso-occlusion, and ultimately end-organ damage. The primary disease pathophysiology is intracellular Hb S polymerization and consequent sickling of erythrocytes. It has become evident for more than several decades that a more complex disease process contributes to the myriad of clinical complications seen in patients with SCD with inflammation playing a central role. Drugs targeting specific inflammatory pathways therefore offer an attractive therapeutic strategy to ameliorate many of the clinical events in SCD. In addition, they are useful tools to dissect the molecular and cellular mechanisms that promote individual clinical events and for developing improved therapeutics to address more challenging clinical dilemmas such as refractoriness to opioids or hyperalgesia. Here, we discuss the prospect of targeting multiple inflammatory pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of SCD with a focus on new therapeutics, striving to link the actions of the anti-inflammatory agents to a defined pathobiology, and specific clinical manifestations of SCD. We also review the anti-inflammatory attributes and the cognate inflammatory targets of hydroxyurea, the only Food and Drug Administration-approved drug for SCD.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors AOA, CAI, AW and SOA declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Embury S, Hebbel RP, Mohandas N, Steinberg MH. Sickle Cell Disease: Basic principles and clinical practice. Raven Press; New York: 1995.
-
- Belcher JD, Mahaseth H, Welch TE, Vilback AE, Sonbol KM, Kalambur VS, et al. Critical role of endothelial cell activation in hypoxia-induced vasoocclusion in transgenic sickle mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288(6):H2715–25. - PubMed
-
- Mahaseth H, Vercellotti GM, Welch TE, Bowlin PR, Sonbol KM, Hsia CJ, et al. Polynitroxyl albumin inhibits inflammation and vasoocclusion in transgenic sickle mice. J Lab Clin Med. 2005;145(4):204–11. - PubMed
-
- Kaul DK, Liu XD, Choong S, Belcher JD, Vercellotti GM, Hebbel RP. Anti-inflammatory therapy ameliorates leukocyte adhesion and microvascular flow abnormalities in transgenic sickle mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;287(1):H293–301. - PubMed
-
- Setty BN, Stuart MJ. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 is involved in mediating hypoxia-induced sickle red blood cell adherence to endothelium: potential role in sickle cell disease. Blood. 1996;88(6):2311–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

