RTN1 mediates progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress
- PMID: 26227493
- PMCID: PMC4532799
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8841
RTN1 mediates progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress
Erratum in
-
Erratum: RTN1 mediates progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress.Nat Commun. 2015 Oct 22;6:8710. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9710. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26489932 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
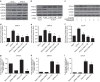
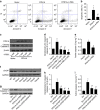
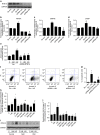
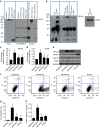
Identification of new biomarkers and drug targets for chronic kidney disease (CKD) is required for the development of more effective therapy. Here we report an association between expression of reticulon 1 (RTN1) and severity of CKD. An isoform-specific increase in the expression of RTN1A is detected in the diseased kidneys from mice and humans, and correlates inversely with renal function in patients with diabetic nephropathy. RTN1 overexpression in renal cells induces ER stress and apoptosis, whereas RTN1 knockdown attenuates tunicamycin-induced and hyperglycaemia-induced ER stress and apoptosis. RTN1A interacts with PERK through its N-terminal and C-terminal domains, and mutation of these domains prevents this effect on ER stress. Knockdown of Rtn1a expression in vivo attenuates ER stress and renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction, and also attenuates ER stress, proteinuria, glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial expansion in diabetic mice. Together, these data indicate that RTN1A contributes to progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress.
Conflict of interest statement
: Microarray data have been deposited in NCBI GEO under accession code GSE69074.
Figures



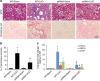
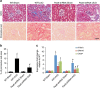
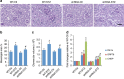
References
-
- Coresh J. et al.. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298, 2038–2047 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Lewis E. J., Hunsicker L. G., Bain R. P. & Rohde R. D. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 329, 1456–1462 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Brenner B. M. et al.. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 861–869 (2001). - PubMed
-
- de Zeeuw D. Unmet need in renal protection--do we need a more comprehensive approach? Contrib. Nephrol. 171, 157–160 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

