Control of signaling-mediated clearance of apoptotic cells by the tumor suppressor p53
- PMID: 26228159
- PMCID: PMC5215039
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1261669
Control of signaling-mediated clearance of apoptotic cells by the tumor suppressor p53
Abstract
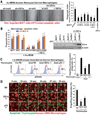
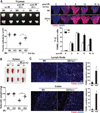
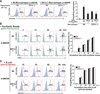
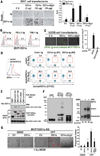
The inefficient clearance of dying cells can lead to abnormal immune responses, such as unresolved inflammation and autoimmune conditions. We show that tumor suppressor p53 controls signaling-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cells through its target, Death Domain1α (DD1α), which suggests that p53 promotes both the proapoptotic pathway and postapoptotic events. DD1α appears to function as an engulfment ligand or receptor that engages in homophilic intermolecular interaction at intercellular junctions of apoptotic cells and macrophages, unlike other typical scavenger receptors that recognize phosphatidylserine on the surface of dead cells. DD1α-deficient mice showed in vivo defects in clearing dying cells, which led to multiple organ damage indicative of immune dysfunction. p53-induced expression of DD1α thus prevents persistence of cell corpses and ensures efficient generation of precise immune responses.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


Comment in
-
CANCER. A p53-regulated immune checkpoint relevant to cancer.Science. 2015 Jul 31;349(6247):476-7. doi: 10.1126/science.aac8475. Science. 2015. PMID: 26228128 No abstract available.
-
Cell death: Tumour suppressor p53 helps phagocytes clean up.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 Sep 15;15(9):525. doi: 10.1038/nri3900. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26250740 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nagata S, Hanayama R, Kawane K. Autoimmunity and the clearance of dead cells. Cell. 2010;140:619–630. pmid: 20211132. - PubMed
-
- Muñoz LE, Lauber K, Schiller M, Manfredi AA, Herrmann M. The role of defective clearance of apoptotic cells in systemic autoimmunity. Rheumatology. 2010;6:280–289. pmid:20431553. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S. Apoptosis and autoimmune diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010;1209:10–16. pmid: 20958310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK057683/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027673/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10RR027673/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095045/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57683/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA142805/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK093378/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK091218/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091218/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043369/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA080058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA142805/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA149477/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062472/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA80058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK062472/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

