Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in rats is accelerated by splenic regulation of liver PTEN/AKT
- PMID: 26228367
- PMCID: PMC4542422
- DOI: 10.4103/1319-3767.161641
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in rats is accelerated by splenic regulation of liver PTEN/AKT
Abstract
Background/aim: The spleen has been reported to participate in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), but the mechanism has not been fully characterized. This study aims to elucidate how the spleen affects the development of NAFLD in a rat model.
Materials and methods: Following either splenectomy or sham operation, male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were fed a high-fat diet to drive the development of NAFLD; animals fed a normal diet were used as controls. Two months after surgery, livers and blood samples were collected. Serum lipids were measured; liver histology, phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) gene expression, and the ratio of pAkt/Akt were determined.
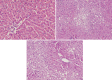
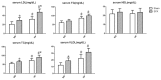
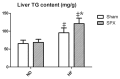
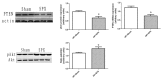
Results: Splenectomy increased serum lipids, except triglyceride (TG) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), in animals fed either a high-fat or normal diet. Furthermore, splenectomy significantly accelerated hepatic steatosis. Western blot analysis and real-time polymerase chain reaction showed splenectomy induced significant downregulation of PTEN expression and a high ratio of pAkt/Akt in the livers.
Conclusions: The spleen appears to play a role in the development of NAFLD, via a mechanism involving downregulation of hepatic PTEN expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ameliorative effects of lutein on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 14;21(26):8061-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8061. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26185377 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of neomangiferin on high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Mar;25(1):218-28. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.01.027. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25661699
-
Fish oil alleviated high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via regulating hepatic lipids metabolism and metaflammation: a transcriptomic study.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Feb 1;15:20. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0190-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 26832365 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Rat Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Constructed Through CRISPR/Cas-Based Hydrodynamic Injection.Mol Biotechnol. 2017 Oct;59(9-10):365-373. doi: 10.1007/s12033-017-0025-8. Mol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28695481
-
The splenic response to stroke: from rodents to stroke subjects.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jul 3;15(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1239-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29970193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog in Non-neoplastic Digestive Disease: More Than Just Tumor Suppressor.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 1;12:684529. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.684529. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34140896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates the NASH phenotype by regulating the miR-375-3p/ATG2B/PTEN-AKT axis to mediate autophagy and pyroptosis.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Feb 10;22(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01787-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 36759837 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model.Open Life Sci. 2022 Jan 29;17(1):22-31. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0004. eCollection 2022. Open Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35128066 Free PMC article.
-
Diet induces hepatocyte protection in fatty liver disease via modulation of PTEN signaling.Biomed Rep. 2020 Jun;12(6):295-302. doi: 10.3892/br.2020.1299. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Biomed Rep. 2020. PMID: 32382414 Free PMC article.
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Challenge from Mechanisms to Therapy.J Clin Med. 2019 Dec 19;9(1):15. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010015. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31861591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Law K, Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2010;14:591–604. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Angulo P. Recent concepts in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabet Med. 2005;22:1129–33. - PubMed
-
- Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology. 1998;114:842–5. - PubMed
-
- Berson A, De Beco V, Letteron P, Robin MA, Moreau C, El Kahwaji J, et al. Steatohepatitis-inducing drugs cause mitochondrial dysfunction and lipid peroxidation in rat hepatocytes. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:764–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
