Bacterial Biofilm Removal Using Static and Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation
- PMID: 26229369
- PMCID: PMC4513774
Bacterial Biofilm Removal Using Static and Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation
Abstract
Background: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficiency of two irrigating techniques - static and dynamic (passive ultrasonic instrumentation) irrigation in the elimination of bacterial biofilm.
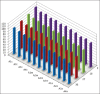
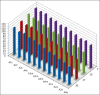
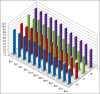
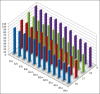
Materials and methods: Forty extracted human permanent maxillary central incisors teeth with straight roots and single canals, were randomly allocated to two groups for static irrigation and passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI). The root canal irrigant used was 2.5 % sodium hypochlorite. The root canals were prepared to tip sizes (20, 40) and tapers (0.04, 0.08). Using system GT instruments (Dentsply Malliefer, Switerzland). The teeth were split longitudinally into two, stained collagen was applied to the canal surfaces and the tooth reassembled for static and PUI. Digital images of the canal surface were taken before and after irrigation with 9, 18, 27 and 37 mL solution. The digital images were analyzed using ImageJ software (National Institute of Health, USA) to quantify residual canal coverage by the stained collagen. The data were analyzed using linear regression models and subjected to statistical analysis.
Results: The mean percentage of canal surface with residual collagen increased with the coronal level of canal, decrease in apical size and taper of canal preparation and decrease in the volume of the irrigant. There was less residual collagen after PUI compared with static irrigation. The canal surface facing the open side port of the needle had less residual collagen after irrigation than the opposing surface.
Conclusion: The stained collagen biomolecular film could not be removed completely either by passive ultrasonic instrumentation or static irrigation. The PUI was found to be more effective in the removal of collagen, especially in the apical part of the root canal.
Keywords: Biofilm; Collagen; irrigation; sodium hypochlorite; ultrasonic.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A bio-molecular film ex-vivo model to evaluate the influence of canal dimensions and irrigation variables on the efficacy of irrigation.Int Endod J. 2008 Jan;41(1):60-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01317.x. Epub 2007 Oct 3. Int Endod J. 2008. PMID: 17916068 Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of dynamic irrigation using a commercially available system (RinsEndo) determined by removal of a collagen 'bio-molecular film' from an ex vivo model.Int Endod J. 2008 Jul;41(7):602-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01408.x. Epub 2008 May 12. Int Endod J. 2008. PMID: 18479371
-
Evaluation of Different Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation Protocols on the Removal of Dentinal Debris from Artificial Grooves.Braz Dent J. 2016 Sep-Oct;27(5):568-572. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440201600725. Braz Dent J. 2016. PMID: 27982235
-
Passive ultrasonic irrigation of the root canal: a review of the literature.Int Endod J. 2007 Jun;40(6):415-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01243.x. Epub 2007 Apr 17. Int Endod J. 2007. PMID: 17442017 Review.
-
Effectiveness of various irrigant activation techniques on the penetration of sodium hypochlorite into lateral canals of mature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Saudi Dent J. 2023 Jan;35(1):1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2022.12.004. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Saudi Dent J. 2023. PMID: 36817024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Biofilm Removal Efficacy by Multisonic Ultracleaning System and Passive Ultrasonic Activation.Materials (Basel). 2019 Oct 25;12(21):3492. doi: 10.3390/ma12213492. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31731396 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Ultrasonic Activation on the Effectiveness of Sodium Hypochlorite: A Review.Iran Endod J. 2015 Fall;10(4):216-20. doi: 10.7508/iej.2015.04.001. Iran Endod J. 2015. PMID: 26525646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiological Evaluation of Penetration of the Irrigant according to Three Endodontic Irrigation Techniques.Int J Dent. 2016;2016:3142742. doi: 10.1155/2016/3142742. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Int J Dent. 2016. PMID: 27433162 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm in Endodontics: In Vitro Cultivation Possibilities, Sonic-, Ultrasonic- and Laser-Assisted Removal Techniques and Evaluation of the Cleaning Efficacy.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Mar 25;14(7):1334. doi: 10.3390/polym14071334. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406207 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ramachandran Nair PN. Light and electron microscopic studies of root canal flora and periapical lesions. J Endod. 1987;13(1):29–39. - PubMed
-
- Nair PN, Henry S, Cano V, Vera J. Microbial status of apical root canal system of human mandibular first molars with primary apical periodontitis after “one-visit” endodontic treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;99(2):231–52. - PubMed
-
- Svensater G, Bergenholtz G. Biofilms in endodontic infections. Endod Top. 2004;9:27–36.
-
- Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284(5418):1318–22. - PubMed
-
- Gu LS, Kim JR, Ling J, Choi KK, Pashley DH, Tay FR. Review of contemporary irrigant agitation techniques and devices. J Endod. 2009;35(6):791–804. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
