IL-2 -330T/G polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 26229483
- PMCID: PMC4514317
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S86136
IL-2 -330T/G polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Some studies have investigated the association of IL-2 -330T/G (rs2069762) polymorphism with cancer risk, but the previous results were conflicting and had relatively low statistical power. Thus, we performed a meta-analysis to derive a more precise estimation of the association between IL-2 -330T/G polymorphism and cancer risk.
Methods: A literature search was performed systematically using electronic databases. The odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to estimate the pooled effect.
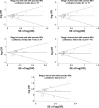
Results: A total of ten studies including 3,060 cases and 3,435 controls were involved in this meta-analysis. The results indicated that IL-2 -330T/G polymorphism was significantly associated with cancer risk ([OR =2.03, 95% CI =1.40-2.95] for GG vs TT; [OR =1.37, 95% CI =1.11-1.69] for GT vs TT; [OR =1.46, 95% CI =1.18-1.81] for [GG + GT] vs TT; [OR =1.66, 95% CI =1.24-2.23] for GG vs [GT + TT]; and [OR =1.35, 95% CI =1.16-1.57] for G vs T). In the subgroup analysis according to cancer type, significant association was found in lymphoma ([OR =1.46, 95% CI =1.11-1.91] for GT vs TT; [OR =1.58, 95% CI =1.22-2.05] for [GG + GT] vs TT; [OR =1.84, 95% CI =1.22-2.77] for GG vs [GT + TT]) and other cancers, but not in gastric cancer. In the subgroup analysis by ethnicity, the significant risk was found among Asians, but not among Europeans.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis suggests that IL-2 -330T/G polymorphism has an increased risk of cancer in Asians. However, further detailed studies are still required to confirm our findings.
Keywords: IL-2; cancer; meta-analysis; polymorphism; risk.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Association between murine double minute 2 T309G polymorphism and risk of liver cancer.Tumour Biol. 2014 Nov;35(11):11353-7. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2432-9. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25119589
-
Lack of association between polymorphism of IL-2 -330T/G and pulmonary tuberculosis among Caucasians.Innate Immun. 2020 Jul;26(5):398-402. doi: 10.1177/1753425919891579. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Innate Immun. 2020. PMID: 31906759 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of association between interleukin-2 (IL-2) gene rs2069762 polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Aug 15;8(8):12557-65. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26550166 Free PMC article.
-
Association between three eNOS polymorphisms and cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(13):5317-24. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.13.5317. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25040995
-
Association of Interleukin-10 Polymorphism (rs1800896, rs1800871, and rs1800872) With Breast Cancer Risk: An Updated Meta-Analysis Based on Different Ethnic Groups.Front Genet. 2022 Feb 4;13:829283. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.829283. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35186043 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori and cytokine gene variants as predictors of premalignant gastric lesions.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 14;25(30):4105-4124. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i30.4105. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31435167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between two interleukin-2 gene polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Apr 19;9:2181-92. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S94761. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27143914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Nelson BH. IL-2, regulatory T cells, and tolerance. J Immunol. 2004;172(7):3983–3988. - PubMed
-
- Abbas KA. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2005.
-
- Miyazaki T, Liu ZJ, Kawahara A, et al. Three distinct IL-2 signaling pathways mediated by bcl-2, c-myc, and lck cooperate in hematopoietic cell proliferation. Cell. 1995;81(2):223–231. - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Ciardelli TL, Russell JH. Partial signaling by cytokines: cytokine regulation of cell cycle and Fas-dependent, activation-induced death in CD4+ subsets. Cell Immunol. 1997;182(2):152–160. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

