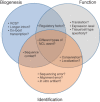
Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs
- PMID: 26230526
- PMCID: PMC5042038
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1294
Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs
Abstract
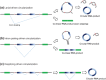
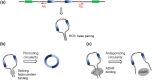
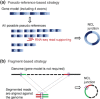
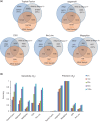
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) arise during post-transcriptional processes, in which a single-stranded RNA molecule forms a circle through covalent binding. Previously, circRNA products were often regarded to be splicing intermediates, by-products, or products of aberrant splicing. But recently, rapid advances in high-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) for global investigation of nonco-linear (NCL) RNAs, which comprised sequence segments that are topologically inconsistent with the reference genome, leads to renewed interest in this type of NCL RNA (i.e., circRNA), especially exonic circRNAs (ecircRNAs). Although the biogenesis and function of ecircRNAs are mostly unknown, some ecircRNAs are abundant, highly expressed, or evolutionarily conserved. Some ecircRNAs have been shown to affect microRNA regulation, and probably play roles in regulating parental gene transcription, cell proliferation, and RNA-binding proteins, indicating their functional potential for development as diagnostic tools. To date, thousands of ecircRNAs have been identified in multiple tissues/cell types from diverse species, through analyses of RNA-seq data. However, the detection of ecircRNA candidates involves several major challenges, including discrimination between ecircRNAs and other types of NCL RNAs (e.g., trans-spliced RNAs and genetic rearrangements); removal of sequencing errors, alignment errors, and in vitro artifacts; and the reconciliation of heterogeneous results arising from the use of different bioinformatics methods or sequencing data generated under different treatments. Such challenges may severely hamper the understanding of ecircRNAs. Herein, we review the biogenesis, identification, properties, and function of ecircRNAs, and discuss some unanswered questions regarding ecircRNAs. We also evaluate the accuracy (in terms of sensitivity and precision) of some well-known circRNA-detecting methods.
© 2015 The Authors. WIREs RNA published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats.RNA. 2013 Feb;19(2):141-57. doi: 10.1261/rna.035667.112. Epub 2012 Dec 18. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23249747 Free PMC article.
-
HNRNPD regulates the biogenesis of circRNAs and the ratio of mRNAs to circRNAs for a set of genes.RNA Biol. 2024 Jan;21(1):1-15. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2386500. Epub 2024 Aug 24. RNA Biol. 2024. PMID: 39180763 Free PMC article.
-
NCLscan: accurate identification of non-co-linear transcripts (fusion, trans-splicing and circular RNA) with a good balance between sensitivity and precision.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Feb 18;44(3):e29. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1013. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26442529 Free PMC article.
-
The Biogenesis, Functions, and Challenges of Circular RNAs.Mol Cell. 2018 Aug 2;71(3):428-442. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.034. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30057200 Review.
-
Circular RNA Splicing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1087:41-52. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30259356 Review.
Cited by
-
Hsa_circ_0109320 Serves as a Novel Circular RNA Biomarker in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Promoting Metastasis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 5. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01306-3. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39499388
-
[CircRNA_005647 inhibits expressions of fibrosis-related genes in mouse cardiac fibroblasts via sponging miR-27b-3p].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Nov 30;39(11):1312-1319. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.11.08. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31852652 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
CircNF1-419 improves the gut microbiome structure and function in AD-like mice.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jan 6;12(1):260-287. doi: 10.18632/aging.102614. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. Retraction in: Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Jul 30;15(14):7333. doi: 10.18632/aging.204905. PMID: 31905172 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Expression alteration of serum exosomal circular RNAs in obstructive sleep apnea patients with acute myocardial infarction.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Mar 9;16(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01464-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36894962 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Study of circRNAs in Hematological Malignancies.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 20;12:900374. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.900374. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35795049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
FURTHER READING
-
- CircBase, a database for circular RNAs, http://circbase.org/. - PMC - PubMed
-
- circ2Traits, a database of human circular RNAs associated with disease or traits, http://gyanxet‐beta.com/circdb/.
-
- TopHat‐Fusion (version 2.0.13), an algorithm for detecting both intergenic and intragenic NCL events, http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/tophat/fusion_index.html.
-
- MapSplice (version 2.17), an algorithm for detecting both intergenic and intragenic NCL events, http://www.netlab.uky.edu/p/bioinfo/MapSplice2.
-
- segemenhl (version 0.2.0), an algorithm for detecting both intergenic and intragenic NCL events (filterjunctions.py was applied to extracting circRNA candidates), http://www.bioinf.uni‐leipzig.de/Software/segemehl/.
References
-
- Grabowski PJ, Zaug AJ, Cech TR. The intervening sequence of the ribosomal RNA precursor is converted to a circular RNA in isolated nuclei of Tetrahymena. Cell 1981, 23:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Lehmann K, Schmidt U. Group II introns: structure and catalytic versatility of large natural ribozymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2003, 38:249–303. - PubMed
-
- Dalgaard JZ, Garrett RA. Protein‐coding introns from the 23S rRNA‐encoding gene form stable circles in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrobaculum organotrophum. Gene 1992, 121:103–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

