New Conclusions Regarding Comparison of Sevelamer and Calcium-Based Phosphate Binders in Coronary-Artery Calcification for Dialysis Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 26230677
- PMCID: PMC4521824
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133938
New Conclusions Regarding Comparison of Sevelamer and Calcium-Based Phosphate Binders in Coronary-Artery Calcification for Dialysis Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Background: Sevelamer hydrochloride is used widely, but its impact upon cardiovascular calcification, cardiovascular mortality, all-cause mortality and hospitalization is not known.
Outcomes: Primary outcome was cardiovascular calcification (coronary artery calcification scores (CACS) and aortic calcification scores (ACS)). Secondary outcomes were serum characteristics, hospitalization, cardiovascular mortality and all-cause mortality. Risk ratio (RR), mean differences and standard mean difference with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were pooled using random- or fixed-effects models.
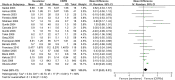
Results: We identified 31 studies (on 23 randomized controlled trials with 4395 participants). An analysis pooling showed a significant decrease in serum levels of phosphate with calcium-based phosphate binders (CBPBs) by 0.17 mg/dL [mean difference (MD), 95% CI, 0.03, 0.31] than sevelamer. A significant difference in the change of CACS by -102.66 [MD: 95% CI, -159.51, -45.80] and ACS by -1008.73 [MD, 95% CI, -1664.75, -352.72] between sevelamer and CBPBs was observed. Prevalence of hypercalcemia (serum levels of calcium >10.2-10.5 mg/dL and >11.0 mg/dL) was significantly smaller for sevelamer (RR = 0.44, 95% CI, 0.33, 0.58; RR = 0.24, 95% CI, 0.14, 0.40). No significant difference was found in hospitalization, all-cause mortality or cardiovascular mortality.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis suggests that sevelamer benefits dialysis patients in terms of CACS, ACS and hypercalcemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Chantrel F, Enache I, Bouiller M, Kolb I, Kunz K, Petitjean P, et al. Abysmal prognosis of patients with type 2 diabetes entering dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. [Journal Article]. 1999. 1999-01-01;14(1):129–36. - PubMed
-
- Tzamaloukas AH, Yuan ZY, Balaskas E, Oreopoulos DG. CAPD in end stage patients with renal disease due to diabetes mellitus—an update. Adv Perit Dial. [Comparative Study; Journal Article]. 1992. 1992-01-19;8:185–91. - PubMed
-
- Brunner FP, Selwood NH. Profile of patients on RRT in Europe and death rates due to major causes of death groups. The EDTA Registration Committee. Kidney Int Suppl. [Journal Article; Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. 1992 1992-10-01;38:S4–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

