DNA End Resection: Nucleases Team Up with the Right Partners to Initiate Homologous Recombination
- PMID: 26231213
- PMCID: PMC4645618
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R115.675942
DNA End Resection: Nucleases Team Up with the Right Partners to Initiate Homologous Recombination
Abstract
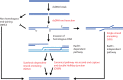
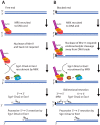
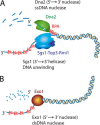
The repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination commences by nucleolytic degradation of the 5'-terminated strand of the DNA break. This leads to the formation of 3'-tailed DNA, which serves as a substrate for the strand exchange protein Rad51. The nucleoprotein filament then invades homologous DNA to drive template-directed repair. In this review, I discuss mainly the mechanisms of DNA end resection in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which includes short-range resection by Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 and Sae2, as well as processive long-range resection by Sgs1-Dna2 or Exo1 pathways. Resection mechanisms are highly conserved between yeast and humans, and analogous machineries are found in prokaryotes as well.
Keywords: DNA end resection; DNA endonuclease; DNA helicase; DNA repair; nuclease; protein phosphorylation; recombination.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- San Filippo J., Sung P., Klein H. (2008) Mechanism of eukaryotic homologous recombination. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 229–257 - PubMed
-
- Shibata A., Moiani D., Arvai A. S., Perry J., Harding S. M., Genois M. M., Maity R., van Rossum-Fikkert S., Kertokalio A., Romoli F., Ismail A., Ismalaj E., Petricci E., Neale M. J., Bristow R. G., Masson J. Y., Wyman C., Jeggo P. A., Tainer J. A. (2014) DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice is directed by distinct MRE11 nuclease activities. Mol. Cell 53, 7–18 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Symington L. S., Gautier J. (2011) Double-strand break end resection and repair pathway choice. Annu. Rev. Genet. 45, 247–271 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

