Development of an indirect ELISA, blocking ELISA, fluorescent microsphere immunoassay and fluorescent focus neutralization assay for serologic evaluation of exposure to North American strains of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
- PMID: 26232106
- PMCID: PMC4522128
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-015-0500-z
Development of an indirect ELISA, blocking ELISA, fluorescent microsphere immunoassay and fluorescent focus neutralization assay for serologic evaluation of exposure to North American strains of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
Abstract
Background: Recent, severe outbreaks of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) in Asia and North America highlight the need for well-validated diagnostic tests for the identification of PEDV infected animals and evaluation of their immune status to this virus. PEDV was first detected in the U.S. in May 2013 and spread rapidly across the country. Some serological assays for PEDV have been previously described, but few were readily available in the U.S. Several U.S. laboratories quickly developed indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) assays for the detection of antibodies to PEDV in swine serum, indicating prior exposure. However, the IFA has several disadvantages, including low throughput and relatively subjective interpretation. Different serologic test formats have advantages and disadvantages, depending on the questions being asked, so a full repertoire of tests is useful. Therefore, the objective of this study was to develop and validate multiple improved serological assays for PEDV, including an indirect ELISA (iELISA); a highly specific monoclonal antibody-based blocking ELISA (bELISA); fluorescent microsphere immunoassays (FMIA) that can be multiplexed to monitor exposure to multiple antigens and pathogens simultaneously; and a fluorescent focus neutralization assay (FFN) to measure functional virus neutralizing antibodies.
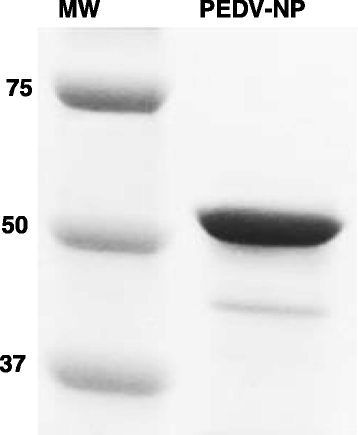
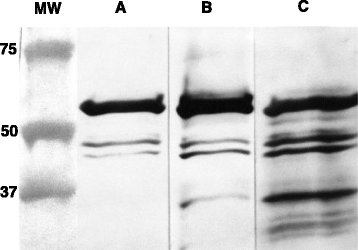
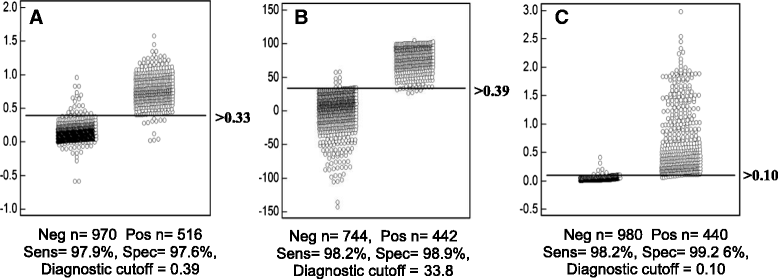
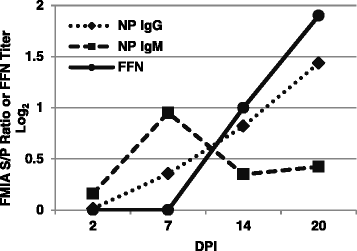
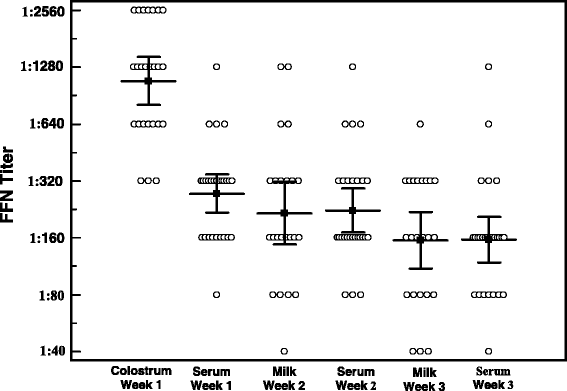
Results: A recombinant North American nucleoprotein (NP) based iELISA was developed and validated along with a bELISA using newly developed PEDV-NP specific biotinylated monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and an FMIA using magnetic beads coupled with expressed NA PEDV-NP. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed using swine serum samples (iELISA n = 1486, bELISA n = 1186, FMIA n = 1420). The ROC analysis for the FMIA showed estimated sensitivity and specificity of 98.2 and 99.2 %, respectively. The iELISA and bELISA showed a sensitivity and specificity of 97.9 and 97.6 %; and 98.2 and 98.9 %, respectively. Inter-rater (kappa) agreement was calculated to be 0.941 between iELISA and IFA, 0.945 between bELISA and IFA and 0.932 between FMIA and IFA. Similar comparative kappa values were observed between the iELISA, bELISA and FMIA, which demonstrated a significant level of testing agreement among the three assays. No cross-reactivity with the closely related coronaviruses, transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) or porcine respiratory coronavirus (PRCV) was noted with these assays. All three assays detected seroconversion of naïve animals within 6-9 days post exposure. The FFN assay allows relative quantitation of functional neutralizing antibodies in serum, milk or colostrum samples.
Conclusion: Well-validated iELISA, bELISA and FMIA assays for the detection of PEDV antibodies were developed and showed good correlation with IFA and each other. Each assay format has advantages that dictate how they will be used in the field. Newly developed mAbs to the PEDV-NP were used in the bELISA and for expediting FFN testing in the detection and quantitation of neutralizing antibodies. In addition, these PEDV mAbs are useful for immunohistochemistry, fluorescent antibody staining and other antigen-based tests. Measurement of neutralizing antibody responses using the FFN assay may provide a valuable tool for assessment of vaccine candidates or protective immunity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of monoclonal antibodies and serological assays including indirect ELISA and fluorescent microsphere immunoassays for diagnosis of porcine deltacoronavirus.BMC Vet Res. 2016 Jun 8;12:95. doi: 10.1186/s12917-016-0716-6. BMC Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27277214 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of serological cross-reactivity and cross-neutralization between the United States porcine epidemic diarrhea virus prototype and S-INDEL-variant strains.BMC Vet Res. 2016 Apr 5;12:70. doi: 10.1186/s12917-016-0697-5. BMC Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27044253 Free PMC article.
-
Development and application of an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant S1 for serological testing of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus.Can J Microbiol. 2019 May;65(5):343-352. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2018-0240. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Can J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30707600
-
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: An overview of current virological and serological diagnostic methods.Virus Res. 2016 Dec 2;226:60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.05.013. Epub 2016 May 14. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27189041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of immunological and genetic methods for detecting swine coronaviruses, transmissible gastroenteritis virus, and porcine respiratory coronavirus in tissues.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;412:37-46. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1828-4_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997. PMID: 9191988 Review.
Cited by
-
Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Promotes SLA-DR-Mediated Antigen Presentation of Nonstructural Proteins To Evoke a Nonneutralizing Antibody Response In Vivo.J Virol. 2020 Oct 14;94(21):e01423-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01423-20. Print 2020 Oct 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32796065 Free PMC article.
-
Specific recombinant proteins of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus are immunogenic, revealing their potential use as diagnostic markers.Vet Microbiol. 2019 Sep;236:108387. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108387. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Vet Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31500721 Free PMC article.
-
Production of virus-like particles of porcine circovirus 2 in baculovirus expression system and its application for antibody detection.BMC Vet Res. 2023 Jul 19;19(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03648-7. BMC Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37468893 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic evaluation of assays for detection of antibodies against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) in pigs exposed to different PEDV strains.Prev Vet Med. 2016 Dec 1;135:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Prev Vet Med. 2016. PMID: 27931933 Free PMC article.
-
A convenient colorimetric assay for the quantification of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and neutralizing antibodies.J Virol Methods. 2018 Dec;262:32-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 12. J Virol Methods. 2018. PMID: 30218684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Debouck P, Pensaert M. Experimental infection of pigs with a new porcine enteric coronavirus, CV 777. Am J Vet Res. 1980;41(2):219–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

