An up-date on health-related quality of life in myasthenia gravis -results from population based cohorts
- PMID: 26232146
- PMCID: PMC4522107
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-015-0298-1
An up-date on health-related quality of life in myasthenia gravis -results from population based cohorts
Abstract
Current available therapies control Myasthenia gravis (MG) reasonably well, but Health Related Quality of life (HRQOL) remains lower than expected. The aim was provide insights in how HRQOL in MG stands across borders and time, compare the scores to general population controls and other chronic disorders and assess the impact of potential predictors for quality of life such as a) clinical characteristics b) antibodies c) thymoma and d) treatment in a population-based cohort.
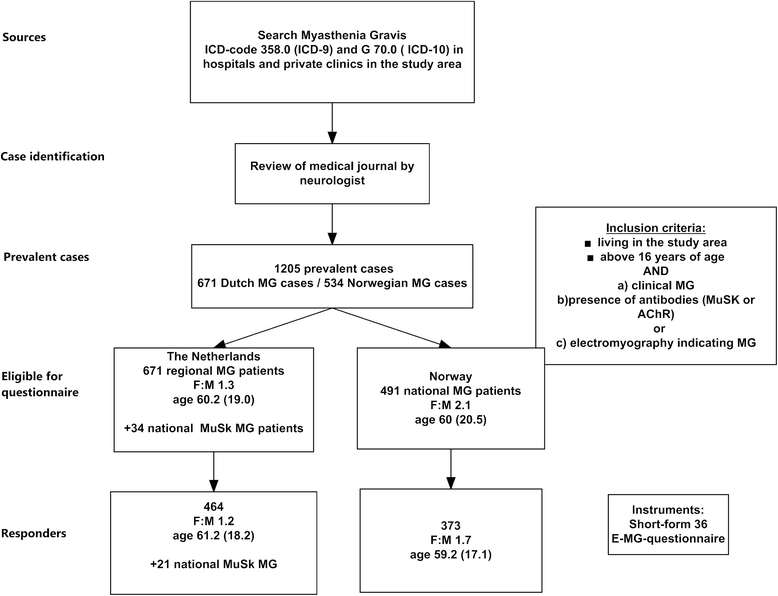
Methods: We designed a population-based cross-sectional study including 858 patients, 373 from Norway and 485 from the Netherlands. The Short Form Health Survey 36 (SF-36) and a cross-cultural validated questionnaire were used. Data were in addition compared to the general population, other chronic diseases and previous studies.
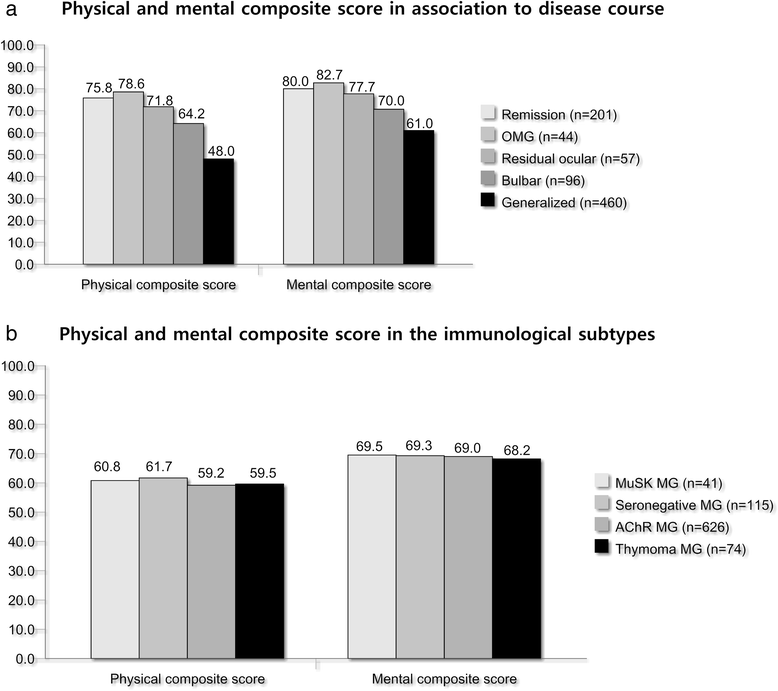
Results: Mean physical composite score was 59.4 and mental composite score 69.0 with no differences between the countries. The mean HRQOL score was lower in patients with bulbar and generalized symptoms (p < 0.001) compared to sex and age adjusted healthy controls, but not in patients with ocular symptoms or patients in remission. Multivariate analysis revealed that female gender, generalized symptoms and use of secondary immunosuppressive drugs at the time of testing were risk factors for reduced HRQOL.
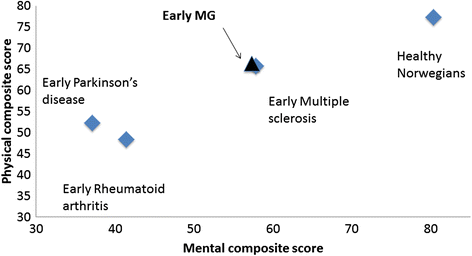
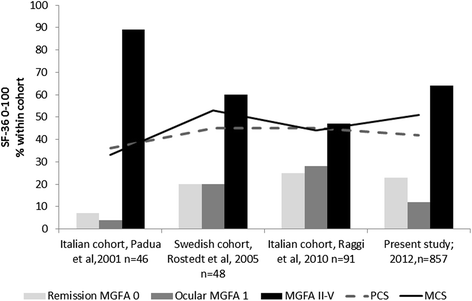
Conclusions: Remission and absence of generalized symptoms were favorable factors for HRQOL in MG patients. Historically, the HRQOL levels have not changed since 2001 and no new clinical predictors could be detected in this exhaustive population-based study. Further studies should explore the impact of non clinical factors like ethnic variations, socio-economic and hormonal factors on HRQOL.
Figures

References
-
- Raggi A, Leonardi M, Antozzi C, Confalonieri P, Maggi L, Cornelio F, et al. Concordance between severity of disease, disability and health-related quality of life in myasthenia gravis. NeurolSci. 2010;31:41–5. - PubMed
-
- Leonardi M, Raggi A, Antozzi C, Confalonieri P, Maggi L, Cornelio F, et al. The relationship between health, disability and quality of life in myasthenia gravis: results from an Italian study. JNeurol. 2010;257:98–102. - PubMed
-
- Rostedt A, Padua L, Stalberg EV. Correlation between regional myasthenic weakness and mental aspects of quality of life. EurJNeurol. 2006;13:191–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

