Telephone Intervention to Improve Diabetes Control: A Randomized Trial in the New York City A1c Registry
- PMID: 26232903
- PMCID: PMC4656092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2015.04.016
Telephone Intervention to Improve Diabetes Control: A Randomized Trial in the New York City A1c Registry
Abstract
Introduction: Scalable self-management interventions are necessary to address suboptimal diabetes control, especially among minority populations. The study tested the effectiveness of a telephone behavioral intervention in improving glycemic control among adults with diabetes in the New York City A1c Registry.
Design: RCT comparing a telephone intervention to print-only intervention in the context of the A1c Registry program.
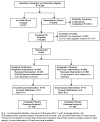
Setting/participants: Nine hundred forty-one adults with diabetes and hemoglobin A1c (A1c) >7% from a low-income, predominantly Latino population in the South Bronx were recruited from the A1c Registry.
Intervention: All study participants were mailed print diabetes self-management materials at baseline and modest lifestyle incentives quarterly. Only the telephone participants received four calls from health educators evenly spaced over 1 year if baseline A1c was >7%-9%, or eight calls if baseline A1c was >9%. Medication adherence was the main behavioral focus and, secondarily, nutrition and exercise.
Main outcome measures: Primary outcome was difference between two study arms in change in A1c from baseline to 1 year. Secondary outcomes included diabetes self-care activities, including self-reported medication adherence. Data were collected in 2008-2012 and analyzed in 2012-2014.
Results: Participants were predominantly Latino (67.7%) or non-Latino black (28%), with 69.7% foreign-born and 55.1% Spanish-speaking. Among 694 (74%) participants with follow-up A1c, mean A1c decreased by 0.9 (SD=0.1) among the telephone group compared with 0.5 (SD=0.1) among the print-only group, a difference of 0.4 (95% CI=0.09, 0.74, p=0.01). The intervention had significant effect when baseline A1c was >9%. Both groups experienced similar improvements in self-care activities, medication adherence, and intensification.
Conclusions: A telephone intervention delivered by health educators can be a clinically effective tool to improve diabetes control in diverse populations, specifically for those with worse metabolic control identified using a registry. This public health approach could be adopted by health systems supported by electronic record capabilities. CLINICALTRIALS.
Gov registration: NCT00797888.
Copyright © 2015 American Journal of Preventive Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
References
-
- Gupta L, Olson C. Epi Data Brief: Diabetes in New York City. Vol. 26. New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene: Epi Data Brief; New York: Apr, 2013.
-
- Thorpe LE, Upadhyay UD, Chamany S, et al. Prevalence and control of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in New York City. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(1):57–62. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc08-0727. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American-Diabetes-Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes - 2013. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(Suppl 1):S11–S66. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc13-S011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chamany S, Silver LD, Bassett MT, et al. Tracking diabetes: New York City's A1C Registry. Milbank Q. 2009;87(3):547–570. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0009.2009.00568.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piatt GA, Orchard TJ, Emerson S, et al. Translating the chronic care model into the community: results from a randomized controlled trial of a multifaceted diabetes care intervention. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(4):811–817. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/diacare.29.04.06.dc05-1785. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical