Impact of cannabis use on prefrontal and parietal cortex gyrification and surface area in adolescents and emerging adults
- PMID: 26233614
- PMCID: PMC5289075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2015.07.004
Impact of cannabis use on prefrontal and parietal cortex gyrification and surface area in adolescents and emerging adults
Abstract
Background: Regions undergoing maturation with CB1 receptors may be at increased risk for cannabis-induced alterations. Here, we examine the relationships between cannabis use and prefrontal (PFC) and inferior parietal gyrification and surface area (SA) in youth.
Methods: Participants included 33 cannabis users and 35 controls (ages 18-25). Exclusions included co-morbid psychiatric/neurologic disorders and heavy other drug use. Multiple regressions and Pearson r correlations examined the effects of cannabis use on gyrification, SA and cognition.
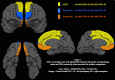
Results: Cannabis use was associated with decreased gyrification in: ventral-medial PFC (RH: [FDR corrected p=.02], LH: [FDR corrected p=.02]); medial PFC (RH: [FDR corrected p=.02], LH: [FDR corrected p=.02]); and frontal poles (RH: [FDR corrected p=.02], LH: [FDR corrected p=.02]). No differences were observed in bilateral hemispheres, PFC, dorsolateral, ventrolateral, or inferior parietal ROIs. Cannabis use was associated with marginally decreased SA in left: medial PFC [FDR corrected p=.09], and ventral lateral PFC: [FDR corrected p=.09]. In cannabis users, increased gyrification was associated with improved working-memory performance in right medial (p=.003), ventral-medial (p=.03), and frontal pole ROIs (p=.007).
Conclusions: Cannabis use was associated with reduced gyrification in PFC regions implicated in self-referential thought and social cognition. Results suggest that these gyrification characteristics may have cognitive implications.
Keywords: Cannabis; Cognition; Emerging adults; Gyrification; Marijuana; Prefrontal and parietal cortex.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bado P., Engel A., Oliveira-Souza R., Bramati I.E., Paiva F.F., Basilio R., Sato J.R., Tovar-Moll F., Moll J. Functional dissociation of ventral frontal and dorsomedial default mode network components during resting state and emotional autobiographical recall. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014;35(7):3302–3313. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartley A.J., Jones D.W., Weinberger D.R. Genetic variability of human brain size and cortical gyral patterns. Brain. 1997;120(2):257–269. - PubMed
-
- Beck A.T., Steer R.A., Brown G.K. Psychological Corporation; San Antonio, TX: 1996. Beck Depression Inventory-II.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

