The effects of moderate exercise on secretory IgA production in mice depends on dietary carbohydrate intake
- PMID: 26236100
- PMCID: PMC4512897
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.15-21
The effects of moderate exercise on secretory IgA production in mice depends on dietary carbohydrate intake
Abstract
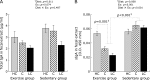
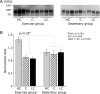
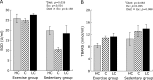
Secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) is produced from intestinal mucosa and is essential in preventing infection. We analyzed the influence of moderate exercise on intestinal sIgA production and antioxidative function under different carbohydrate nutritional conditions. Thirty-six mice were fed an experimental diet for 10 weeks-a high-carbohydrate (HC) diet, a low-carbohydrate (LC) diet, or a control (C) diet. After 1 week on the experimental diets, mice were divided into sedentary and exercise groups (n = 6/group), where the exercise consisted of treadmill running for 30 min/day at 11 m/min for 6 days/week in 9 consecutive weeks. Intestinal sIgA levels in the exercise groups fed C or LC diets were significantly lower compared with the parallel sedentary groups, or exercise-group mice fed HC diet. Expression of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) in the small intestine was significantly higher in the exercise group fed a HC diet. Superoxide dismutase activity in the small intestine was higher in the exercise group than in the sedentary group, with no effects resulting from intake carbohydrate levels. Our results indicated that moderate exercise reduced the levels of intestinal sIgA depending on decreasing of carbohydrate intake, which is connected with the expression of pIgR.
Keywords: SOD; carbohydrate intake; moderate exercise; pIgR; sIgA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects on secretory IgA levels in small intestine of mice that underwent moderate exercise training followed by a bout of strenuous swimming exercise.Brain Behav Immun. 2012 Nov;26(8):1300-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.07.018. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Brain Behav Immun. 2012. PMID: 22884415
-
Intestinal polymeric immunoglobulin receptor is affected by type and route of nutrition.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2007 Sep-Oct;31(5):351-6; discussion 356-7. doi: 10.1177/0148607107031005351. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17712142
-
Depression in the quantity of intestinal secretory IgA and in the expression of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor in caloric deficiency of the weanling mouse.Lab Invest. 1998 Oct;78(10):1255-66. Lab Invest. 1998. PMID: 9800951
-
Moderate exercise enhances expression of SIgA in mouse ileum.Int J Sports Med. 2012 Dec;33(12):1020-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1312607. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Int J Sports Med. 2012. PMID: 22706946
-
Reduced Expression of Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptors in the Intestine of Young Rats Fed a Fiber-free Diet.Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2012;31(3):51-8. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.31.51. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2012. PMID: 24936349 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-invasive Assessment of Fecal Stress Biomarkers in Hunting Dogs During Exercise and at Rest.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Apr 21;7:126. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00126. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32373631 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Chair-Based Exercises Improve Functional Fitness, Mental Well-Being, Salivary Steroid Balance, and Anti-microbial Activity in Pre-frail Older Women.Front Psychol. 2021 Mar 25;12:564490. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.564490. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33841224 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate Aerobic Exercise Induces Homeostatic IgA Generation in Senile Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 27;25(15):8200. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158200. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125769 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate exercise prevents neurodegeneration in D-galactose-induced aging mice.Neural Regen Res. 2016 May;11(5):807-15. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.182709. Neural Regen Res. 2016. PMID: 27335566 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in salivary flow rate following Chlorella-derived multicomponent supplementation.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2016 Jul;59(1):45-8. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.16-3. Epub 2016 May 21. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27499578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mackinnon LT. Chronic exercise training effects on immune function. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32:S369–S376. - PubMed
-
- Klentrou P, Cieslak T, MacNeil M, Vintinner A, Plyley M. Effect of moderate exercise on salivary immunoglobulin A and infection risk in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2002;87:153–158. - PubMed
-
- Smith TP, Kennedy SL, Fleshner M. Influence of age and physical activity on the primary in vivo antibody and T cell-mediated responses in men. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2004;97:491–498. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu K, Kimura F, Akimoto T, Akama T, Kuno S, Kono I. Effect of free-living daily physical activity on salivary secretory IgA in elderly. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39:593–598. - PubMed
-
- Fehr HG, Lötzerich H, Michna H. The influence of physical exercise on peritoneal macrophage functions: histochemical and phagocytic studies. Int J Sports Med. 1988;9:77–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

