Antisense oligonucleotides against microRNA-21 reduced the proliferation and migration of human colon carcinoma cells
- PMID: 26236156
- PMCID: PMC4522075
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-015-0228-7
Antisense oligonucleotides against microRNA-21 reduced the proliferation and migration of human colon carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Colon carcinoma is one of the commonly tumors that threaten human beings as its highly morbidity and mortality. Recent evidences suggested that microRNA-21 (miR-21) played an important role in the development of colon carcinoma and might be a potential biological marker for the diagnosis and prognosis of colon carcinoma. However, the potential effect of miR-21 based therapeutic studies in colon carcinoma remains to be fully elucidated.
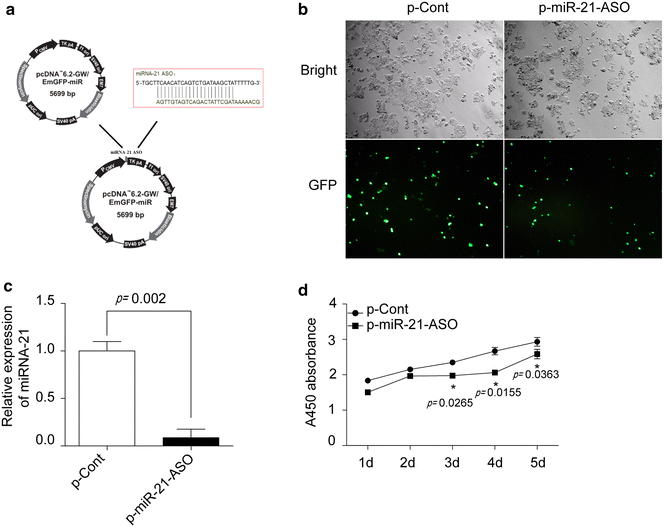
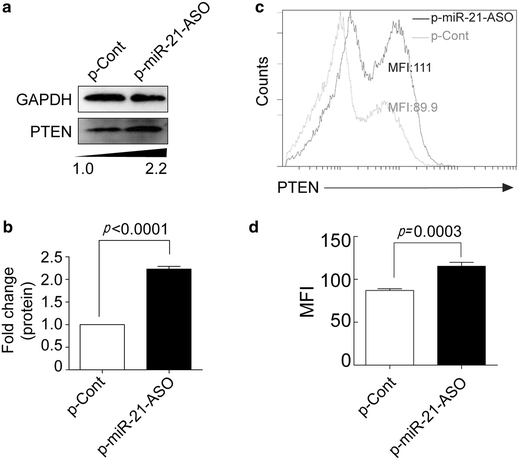
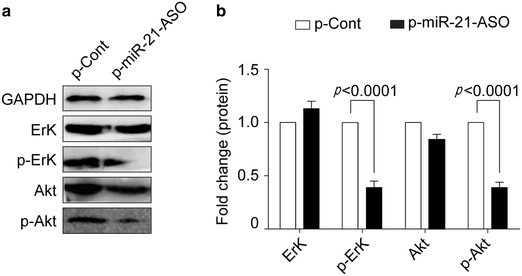
Methods: In present study, we constructed an eukaryotic expression vector encoding antisense oligonucleotides against miR-21 (termed as p-miR-21-ASO) and the expression of miRNA-21 in human colon cancer was detected by Real-time PCR. To assess its possible effect on the proliferation and migration capacity of human colon carcinoma cells in vitro, CCK-8 assay, colony formation assay and cell invasion, as well as migration assay, were performed respectively. Moreover, PTEN, one of target molecules of miRNA-21, was analyzed by Western blot and Fluorescence activated cell sorter assay. Finally, the transduction of AKT and ERK pathways in human colon carcinoma cells was determined by Western blot.
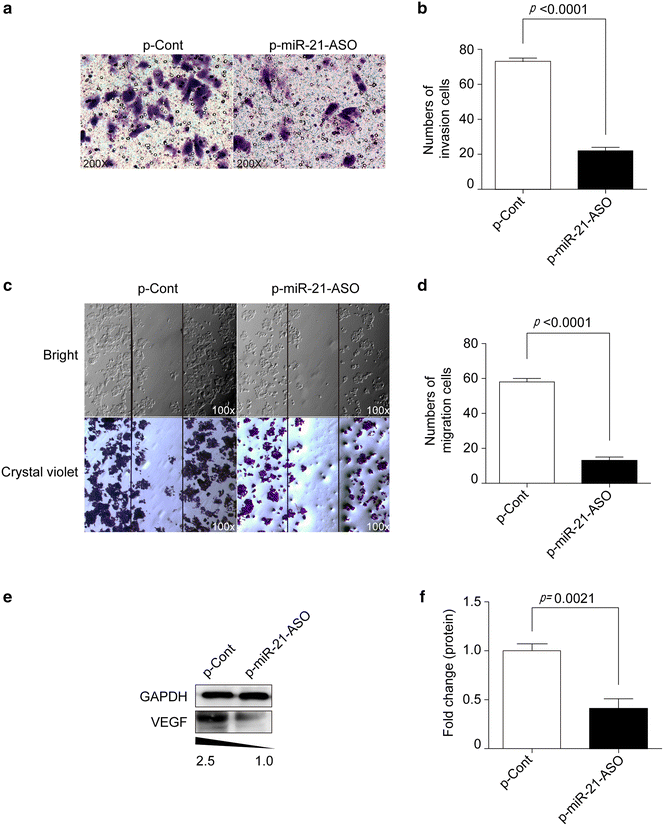
Results: We found that transiently transfection of p-miR-21-ASO could efficiently decrease the relative expression of miR-21 in human colon carcinoma HCT116 cells, accompanied by impaired proliferation and clone formation. Furthermore, we found that down-regulation of miR-21 also could significantly abrogate the invasion and migration capacity in vitro, as well as the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor which is critical for the metastatic capacity of colon carcinoma cells. Mechanistic evidence showed that down-regulation of miR-21 increased the expression of its target molecule PTEN in HCT116 cells. Finally, we revealed that the expression level of both phosphor-ERK1/2 and phosphor-AKT also were altered.
Conclusions: Therefore, our data suggested miR-21 ASO against miR-21 might be a useful strategy to alter the expression of miR-21 in colon carcinoma cells, which was helpful for the development of miR-21-based therapeutic strategies against clinical colon carcinoma.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotides (ASO); Colon carcinoma; MicroRNA-21; Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN).
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-21 (Mir-21) Promotes Cell Growth and Invasion by Repressing Tumor Suppressor PTEN in Colorectal Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):945-958. doi: 10.1159/000481648. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28957811
-
MicroRNA-106b promotes pituitary tumor cell proliferation and invasion through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by targeting PTEN.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):13469-13477. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5155-2. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27465551
-
Inhibition of microRNA-21 increases radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells through phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 activation.Dis Esophagus. 2013 Nov-Dec;26(8):823-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2012.01389.x. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Dis Esophagus. 2013. PMID: 22958183
-
MicroRNA-152 Targets Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog to Inhibit Apoptosis and Promote Cell Migration of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Nov 13;22:4330-4337. doi: 10.12659/MSM.898110. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27840403 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-132 promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of human pancreatic carcinoma by inhibition of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019 Nov;148:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 28941804 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Roles in the Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway in Cancer.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 19;9:546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00546. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29616037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in the Differential Diagnosis of Lipomatous Tumors and Their Mimics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 15;23(14):7804. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147804. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887151 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma miR-21 expression: an indicator for the severity of Type 2 diabetes with diabetic retinopathy.Biosci Rep. 2017 Mar 27;37(2):BSR20160589. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160589. Print 2017 Apr 28. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28108673 Free PMC article.
-
FKBP14 Promotes The Proliferation And Migration Of Colon Carcinoma Cells Through Targeting IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Nov 1;12:9069-9076. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S222555. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31802914 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21: A promising biomarker for the prognosis and diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):2777-2782. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8972. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

