State-of-art neuroanatomical target analysis of high-definition and conventional tDCS montages used for migraine and pain control
- PMID: 26236199
- PMCID: PMC4502355
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00089
State-of-art neuroanatomical target analysis of high-definition and conventional tDCS montages used for migraine and pain control
Abstract
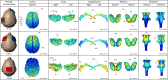
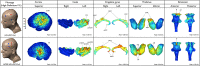
Although transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) studies promise to modulate cortical regions associated with pain, the electric current produced usually spreads beyond the area of the electrodes' placement. Using a forward-model analysis, this study compared the neuroanatomic location and strength of the predicted electric current peaks, at cortical and subcortical levels, induced by conventional and High-Definition-tDCS (HD-tDCS) montages developed for migraine and other chronic pain disorders. The electrodes were positioned in accordance with the 10-20 or 10-10 electroencephalogram (EEG) landmarks: motor cortex-supraorbital (M1-SO, anode and cathode over C3 and Fp2, respectively), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (PFC) bilateral (DLPFC, anode over F3, cathode over F4), vertex-occipital cortex (anode over Cz and cathode over Oz), HD-tDCS 4 × 1 (one anode on C3, and four cathodes over Cz, F3, T7, and P3) and HD-tDCS 2 × 2 (two anodes over C3/C5 and two cathodes over FC3/FC5). M1-SO produced a large current flow in the PFC. Peaks of current flow also occurred in deeper brain structures, such as the cingulate cortex, insula, thalamus and brainstem. The same structures received significant amount of current with Cz-Oz and DLPFC tDCS. However, there were differences in the current flow to outer cortical regions. The visual cortex, cingulate and thalamus received the majority of the current flow with the Cz-Oz, while the anterior parts of the superior and middle frontal gyri displayed an intense amount of current with DLPFC montage. HD-tDCS montages enhanced the focality, producing peaks of current in subcortical areas at negligible levels. This study provides novel information regarding the neuroanatomical distribution and strength of the electric current using several tDCS montages applied for migraine and pain control. Such information may help clinicians and researchers in deciding the most appropriate tDCS montage to treat each pain disorder.
Keywords: HD-tDCS; finite-element modeling; neuromodulation; pain; transcranial direct current stimulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variation of cerebrospinal fluid in specific regions regulates focality in transcranial direct current stimulation.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Sep 2;16:952602. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.952602. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36118967 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing electrode placement for transcranial direct current stimulation in nonsuperficial cortical regions: a computational modeling study.Biomed Eng Lett. 2023 Nov 23;14(2):255-265. doi: 10.1007/s13534-023-00335-2. eCollection 2024 Mar. Biomed Eng Lett. 2023. PMID: 38374912 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Cathode Location and the Size of Anode on Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Over the Leg Motor Area in Healthy Humans.Front Neurosci. 2018 Jul 4;12:443. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00443. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30022928 Free PMC article.
-
The Concept, Development, and Application of a Home-Based High-Definition tDCS for Bilateral Motor Cortex Modulation in Migraine and Pain.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 7;3:798056. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2022.798056. eCollection 2022. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35295794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroimaging and neuromodulation approaches to study eating behavior and prevent and treat eating disorders and obesity.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Mar 24;8:1-31. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.03.016. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26110109 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of online tDCS to left somatomotor cortex on neuropsychiatric symptoms among older adults at risk for dementia.Cortex. 2023 Feb;159:131-141. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2022.10.015. Epub 2022 Dec 17. Cortex. 2023. PMID: 36623419 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of transcranial direct current stimulation and transcranial magnetic stimulation for chronic orofacial pain: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 15;14(8):e0221110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221110. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31415654 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation and Monoclonal Antibodies Acting on the CGRP as a Combined Treatment for Migraine (TACTIC): Protocol for a Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Trial.Front Neurol. 2022 May 10;13:890364. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.890364. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35620782 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the effects of anodal and cathodal high definition transcranial direct current stimulation targeting the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 13;8(1):4454. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22730-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29535340 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic Migraine Preventive Treatment by Prefrontal-Occipital Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS): A Proof-of-Concept Study on the Effect of Psychiatric Comorbidities.Front Neurol. 2021 May 13;12:654900. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.654900. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34079513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amassian V. E., Maccabee P. J., Cracco R. Q., Cracco J. B., Somasundaram M., Rothwell J. C., et al. . (1994). The polarity of the induced electric field influences magnetic coil inhibition of human visual cortex: implications for the site of excitation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 93, 21–26. 10.1016/0168-5597(94)90087-6 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

