Rare Presentation of Gall Bladder Tuberculosis in a Non Immuno-Compromised Patient
- PMID: 26236458
- PMCID: PMC4500880
- DOI: 10.4081/cp.2015.754
Rare Presentation of Gall Bladder Tuberculosis in a Non Immuno-Compromised Patient
Abstract
The gall bladder is least common intra-abdominal organ to be involved by tuberculosis. It is either part of systemic miliary tuberculosis or abdominal tuberculosis. Isolated gall bladder tuberculosis is even rarer, can presents either as calculus or acalculus cholecystitis. Gall bladder tuberculosis presenting as a localized perforation with a sinus formation into anterior abdominal wall is unreported complication in a non immuno-compromised person. A 48-year old female presented with a gradually increasing swelling in right hypochondrium. Abdominal ultrasound showed superficial collection over right hypochondrium with intraperitoneal extension. Computed tomography showed localized gall bladder perforation with extension to the abdominal wall. Patient underwent emergency exploration and cholecystectomy with excision of sinus tract and drainage of abdominal wall abscess. Histopathological examination showed granulomatous cholecystitis suggestive of tuberculosis of gall bladder with extension into the sinus tract. She had an uneventful recovery and was treated with 6-month antitubercular therapy after surgery.
Keywords: Gall bladder tuberculosis; gall bladder perforation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
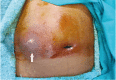

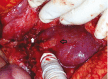


References
-
- Rejab H, Guirat A, Ellouze S, et al. Primitive gallbladder tuberculosis: a case report with review of the literature. Ann Ital Chir 2013;84:1-3. - PubMed
-
- Sharma S, Bansal R, Agrawal N, et al. Tuberculosis of the gall bladder clinically mimicking carcinoma - a case report. J Indian Med Assoc 2012;110:402-3. - PubMed
-
- Ryu MJ, Jeon TJ, Park JY, et al. A case of gallbladder tuberculosis diagnosed by positive tuberculosis-polymerase chain reaction. Korean J Gastroenterol 2014;63:51-5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
